Long non-coding RNAs in anti-cancer drug resistance
- PMID: 27713133
- PMCID: PMC5352108
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.12461
Long non-coding RNAs in anti-cancer drug resistance
Abstract
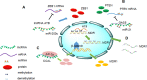
Chemotherapy is one of the basic treatments for cancers; however, drug resistance is mainly responsible for the failure of clinical treatment. The mechanism of drug resistance is complicated because of interaction among various factors including drug efflux, DNA damage repair, apoptosis and targets mutation. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been a focus of research in the field of bioscience, and the latest studies have revealed that lncRNAs play essential roles in drug resistance in breast cancer, gastric cancer and lung cancer, et al. Dysregulation of multiple targets and pathways by lncRNAs results in the occurrence of chemoresistance. In this review, we will discuss the mechanisms underlying lncRNA-mediated resistance to chemotherapy and the therapeutic potential of lncRNAs in future cancer treatment.
Keywords: cancer; chemotherapy; drug resistance; long non-coding RNAs; targets.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Spitzweg C, Morris JC, Bible KC. New drugs for medullary thyroid cancer: new promises? Endocr Relat Cancer. 2016;23:R287–297. - PubMed
-
- Kuwano M, Sonoda K, Murakami Y, Watari K, Ono M. Overcoming drug resistance to receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Learning from lung cancer. Pharmacol Therapeut. 2016;161:97–110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

