A novel Fe(III) dependent bioflocculant from Klebsiella oxytoca GS-4-08: culture conditions optimization and flocculation mechanism
- PMID: 27713559
- PMCID: PMC5054519
- DOI: 10.1038/srep34980
A novel Fe(III) dependent bioflocculant from Klebsiella oxytoca GS-4-08: culture conditions optimization and flocculation mechanism
Abstract
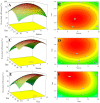
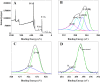
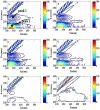
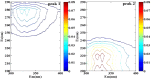
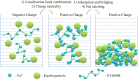
In this work, the effect of cultivation factors on the flocculation efficiency (FE) of bioflocculant P-GS408 from Klebsiella oxytoca was optimized by the response surface methodology. The most significant factor, i.e. culture time, was determined by gray relational analysis. A total of 240 mg of purified P-GS408 was prepared from 1 liter of culture solution under the optimal conditions. GC-MS analysis results indicated that the polysaccharide of P-GS408 mainly contains Rhamnose and Galactose, and the existence of abundant hydroxyl, carboxyl and amino groups was evidenced by FTIR and XPS analyses. With the aid of Fe3+, the FE of kaolin solution by P-GS408 could achieve 99.48% in ten minutes. Functional groups of polysaccharide were involved in the first adsorption step and the zeta potential of kaolin solution changed from -39.0 mV to 43.4 mV in the presence of Fe3+ and P-GS408. Three-dimensional excitation-emission (EEM) fluorescence spectra demonstrates that the trivalent Fe3+ and Al3+ can bind efficiently with P-GS408, while those univalent and divalent cations cannot. With the help of SEM images, FTIR, zeta potential and EEM spectra, we proposed the P-GS408 flocculation mechanism, which consists of coordination bond combination, charge neutrality, adsorption and bridging, and net catching.
Figures


References
-
- Xia S. Q. et al. Production and characterization of a bioflocculant by Proteus mirabilis TJ-1. Bioresource Technol 99, 6520–6527 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Aljuboori A. H. R., Idris A., Abdullah N. & Mohamad R. Production and characterization of a bioflocculant produced by Aspergillus flavus. Bioresource Technol 127, 489–493 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Wang S. G. et al. Production of a novel bioflocculant by culture of Klebsiella mobilis using dairy wastewater. Biochem Eng J 36, 81–86 (2007).
-
- Giri S. S., Harshinya M., Sen S. S., Sukumaran V. & Park S. C. Production and characterization of a thermostable bioflocculant from Bacillus subtilis F9, isolated from wastewater sludge. Ecotox Environ Safe 121, 45–50 (2015). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

