The difference in correlation between insulin resistance index and chronic inflammation in type 2 diabetes with and without metabolic syndrome
- PMID: 27713874
- PMCID: PMC5046740
- DOI: 10.4103/2277-9175.188489
The difference in correlation between insulin resistance index and chronic inflammation in type 2 diabetes with and without metabolic syndrome
Abstract
Background: Insulin resistance (IR) is associated with low-grade systemic inflammation. It plays an important role in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and cardiovascular disease (CVD) in patients with metabolic syndrome (MetS). It is unclear whether diabetic patients with MetS confer elevated CVD risk and outcomes beyond the impact of individual's components of MetS. The aim of this study is to highlight the central role of IR, inflammation, triglyceride/high-density lipoprotein- cholesterol (TG/HDL-C) ratio, and atherogenic index of plasma (AIP) in T2DM with MetS.
Materials and methods: This cross-sectional study comprised 130 men distributed into three groups, namely Controls: 40 nondiabetic healthy volunteers; Group I: 40 T2DM patients without MetS, and Group II: 50 T2DM patients with MetS. Fasting blood samples were collected for the measurement of blood lipid profile, glucose, insulin, hemoglobin A1c, and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP). TG/HDL-C ratio, AIP, and homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) were calculated.
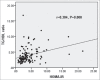
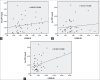
Results: Significant positive association was observed between HOMA-IR and hs-CRP only in Group II and between HOMA-IR and TG/HDL-C ratio in all subjects. Significant differences were seen in waist and hip circumferences, waist/hip ratio, body mass index, systolic blood pressure, fasting blood glucose, TGs, HDL-C, insulin, hs-CRP, HOMA-IR, TG/HDL ratio, and AIP between Controls and Group I with Group II.
Conclusions: In T2DM with MetS, coexistence of elevated atherogenic indices, systemic inflammation, and association between HOMA-IR and TG/HDL-C ratio were seen. These factors are considered having important role in elevated CVD risk beyond MetS components in these patients.
Keywords: Atherogenic index of plasma; inflammation; insulin resistance index; metabolic syndrome; triglyceride/high-density lipoprotein -cholesterol ratio; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Figures

References
-
- Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults. Executive Summary of The Third Report of The National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol In Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) JAMA. 2001;285:2486–97. - PubMed
-
- Haffner SM. The metabolic syndrome: Inflammation, diabetes mellitus, and cardiovascular disease. Am J Cardiol. 2006;97:3A–11A. - PubMed
-
- Kahn SE, Zinman B, Haffner SM, O’Neill MC, Kravitz BG, Yu D, et al. Obesity is a major determinant of the association of C-reactive protein levels and the metabolic syndrome in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2006;55:2357–64. - PubMed
-
- Freeman DJ, Norrie J, Caslake MJ, Gaw A, Ford I, Lowe GD, et al. C-reactive protein is an independent predictor of risk for the development of diabetes in the West of Scotland Coronary Prevention Study. Diabetes. 2002;51:1596–600. - PubMed
-
- Esser N, Legrand-Poels S, Piette J, Scheen AJ, Paquot N. Inflammation as a link between obesity, metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2014;105:141–50. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

