Contemporary experience with high-dose interleukin-2 therapy and impact on survival in patients with metastatic melanoma and metastatic renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 27714434
- PMCID: PMC5099373
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-016-1910-x
Contemporary experience with high-dose interleukin-2 therapy and impact on survival in patients with metastatic melanoma and metastatic renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
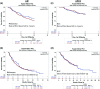
High-dose interleukin-2 (HD IL-2) was approved for treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) in 1992 and for metastatic melanoma (mM) in 1998, in an era predating targeted therapies and immune checkpoint inhibitors. The PROCLAIMSM registry was established to collect and analyze data for patients treated with HD IL-2 in the current era. This analysis includes 170 patients with mM and 192 patients with mRCC treated between 2005 and 2012 with survival data current as of July 27, 2015. For patients with mM, complete response (CR) was observed in 5 %, partial response (PR) in 10 %, stable disease (SD) in 22 %, and 63 % had progressive disease (PD). The median overall survival (mOS) for these patients was 19.6 months, with a median follow-up of 43.1 months. The mOS was not reached for patients achieving CR or PR, and was 33.4 months for patients with SD. For patients with mRCC, 6 % achieved CR, 9 % had PR, 22 % had SD, and 62 % had PD. The mOS was 41 months, with a median follow-up of 46.6 months. The mOS for patients who had CR and PR was not reached and was 49.6 months for patients with SD. There were no treatment-related deaths among 362 patients. The duration of mOS for patients with mM and mRCC is longer than historically reported. These data support a continued role for IL-2 in the treatment of eligible patients with mM or mRCC and warrant further evaluation of HD IL-2 in combination or sequence with other therapeutic agents.
Keywords: Immunotherapy; Interleukin-2; Melanoma; Renal cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
M. Wong, J. Clark, D. McDermott, H. Kaufman, G. Daniels, M. Morse, and J. Dutcher, author(s) of this publication serve as consultants for Prometheus Laboratories Inc., which markets the product related to the research being reported. A. Alva served as an advisory board member for Bayer, Eisai and Prometheus and has received research funding from Bayer, Genentech, Novartis, Sanofi-Aventis, BMS, and Prometheus. H. Kaufman has received honoraria from Alkermes, Amgen, EMD Serono, Merck, Prometheus and Sanofi; served as an advisory board member at Prometheus and consultant for Alkermes, Amgen, EMD Serono, Merck and Sanofi; and served on the Merck Speaker’s Bureau. A. Morse has received honoraria from Genentech, Prometheus, Celgene, Ipsen, Novartis, and Lexxicon; has served as an advisory board member for Genentech, Prometheus, Celgene, Ipsen, Novartis, and Lexxicon; and served on the speaker’s board of Genentech, Prometheus, Celgene, and Novartis. J. Clark has received honoraria from Prometheus, BMS, Pfizer and Merck; has served as an advisory board member for Prometheus and Bayer-Onyx; and served on the speaker’s bureau for Prometheus, BMS and Merck. R. Hauke has received honoraria from Best Doctors for second opinion consultations. B. Curti has received honoraria from Prometheus; is an unpaid consultant for Agonox and Ubivac; served on the speaker’s bureau for Prometheus; has research support from Prometheus and Galectin Therapeutics; and received travel reimbursement from Agonox, BMS and Prometheus. R. Gonzalez has served as advisory board member for Bayer-Onyx, BMS, Genentech, GSK, Prometheus, Roche; has received research funding from Bayer, BMS, Eisai, Genentech, GSK, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Prometheus, Roche. M. Fishman has Research support in RCC-related trials from Acceleron, Altor, Aveo, Bayer, Eisai, Exelixis, GSK (now part of Novartis), Merck, Pfizer, Prometheus, Tracon; and participated in RCC-related advisory boards for Aveo, Bayer, Eisai, GSK (now part of Novartis), Novartis, Pfizer, Prometheus. T. Logan has served as consulting or advisory role for Argos, Aveo, Bristo Myers Squibb, Celgene, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Pfizer, Prometheus, Wyeth; is on speaker’s bureau for BMS, GSK, Novartis, Pfizer, Prometheus; and has research funding from Abbott Labs, Abraxis, Acceleron, Amgen, Argos, AstraZeneca, Aveo, Biovex, BMS, Eisai, Eli Lilly, GSK, Hoffman-LaRoche, Immatics, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Prometheus, Roche, Synta, Threshold Pharmaceuticals, Millenium, Tracon, Cerulean, EMD Serono. JP Dutcher serves on speaker’s bureaus for Prometheus, Novartis, Pfizer; serves as consultant to Prometheus, Nektar, Lion; serves on data safety and monitoring boards for BMS, Tracon, PrECOG. H. Hua is an employee of Prometheus Laboratories Inc. S. Aung was an employee of Prometheus Laboratories Inc. and is currently an employee of Nektar Therapeutics. All other authors declare no conflict of interest. Ethical approval All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. For this type of study formal consent is not required.
Figures

References
-
- Fyfe G, Fisher RI, Rosenberg SA, Sznol M, Parkinson DR, Louie AC. Results of treatment of 255 patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma who received high-dose recombinant interleukin-2 therapy. J Clin Oncol. 1995;13:688–696. - PubMed
-
- Atkins MB, Lotze MT, Dutcher JP, Fisher RI, Weiss G, Margolin K, Abrams J, Sznol M, Parkinson D, Hawkins M, Paradise C, Kunkel L, Rosenberg SA. High-dose recombinant interleukin 2 therapy for patients with metastatic melanoma: analysis of 270 patients treated between 1985 and 1993. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:2105–2116. - PubMed
-
- Fisher RI, Rosenberg SA, Fyfe G. Long-term survival update for high-dose recombinant interleukin-2 in patients with renal cell carcinoma. Cancer J Sci Am. 2000;6(Suppl 1):S55–S57. - PubMed
-
- Payne R, Glenn L, Hoen H, Richards B, Smith JW, 2nd, Lufkin R, Crocenzi TS, Urba WJ, Curti BD. Durable responses and reversible toxicity of high-dose interleukin-2 treatment of melanoma and renal cancer in a Community Hospital Biotherapy Program. J Immunother Cancer. 2014;2:2–13. doi: 10.1186/2051-1426-2-13. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

