Predictive factors of bleeding events in adults undergoing extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
- PMID: 27714705
- PMCID: PMC5053950
- DOI: 10.1186/s13613-016-0196-7
Predictive factors of bleeding events in adults undergoing extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
Abstract
Background: Bleeding is the most frequent complication associated with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) support in critically ill patients. Nonetheless, risk factors for bleeding have been poorly described especially those associated with coagulation anomalies and anticoagulant therapy during ECMO support. The aim of this study is to describe bleeding complications in critically ill patients undergoing ECMO and to identify risk factors for bleeding events.
Methods: We retrospectively analysed ICU charts of adults who received either veno-venous (VV) or veno-arterial (VA) ECMO support in two participating ICUs between 2010 and 2013. Characteristics of patients with and without bleeding complications, as per the Extracorporeal Life Support Organisation (ELSO) definition, were compared, and the impact of bleeding complications on patient outcomes was assessed using survival analysis. Variables that were independently associated with bleeding, including daily clinical and biological variables during ECMO courses, were modelled.
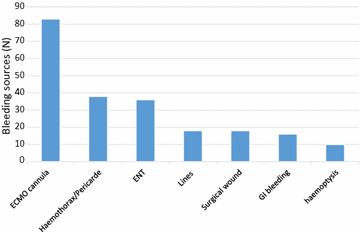
Results: Of the 149 ECMO episodes (111 VA ECMO and 38 VV ECMO) performed in 147 adults, 89 episodes (60 %) were complicated by at least one bleeding event. The most common bleeding sources were: ECMO cannula (37 %), haemothorax or cardiac tamponade (17 %) and ear-nose and throat (16 %). Intra-cranial haemorrhage occurred in five (2.2 %) patients. Bleeding complications were independently associated with worse survival [adjusted hazard ratio (HR) 2.17, 95 % confidence interval (CI) 1.07-4.41, P = 0.03]. Higher activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) [adjusted odds ratio (OR) 3.00, 95 % CI 1.64-5.47, P < 0.01], APACHE III score [adjusted OR 1.01, 95 % CI 1.01-1.02, P = 0.01] and ECMO following surgery [adjusted OR 3.04, 95 % CI 1.62-5.69, P < 0.01] were independently associated with greater risk of bleeding occurrence. A similar association between bleeding and higher aPTT was found when non-post-surgical VA ECMO was considered separately.
Conclusions: Bleeding events based on the ELSO bleeding definition occurred in more than 60 % of ECMO episodes and were associated with hospital mortality. We identified higher aPTT prior bleeding as an independent risk factor for bleeding event, suggesting that better control of the aPTT (through a better control of either coagulopathy or anticoagulation) may improve patients' outcome.
Keywords: Anticoagulation; Bleeding; Coagulopathy; Critically ill patients; Extra corporeal membrane oxygenation; Haemorrhage; Thromboembolic events.
Figures
References
-
- Zangrillo A, Landoni G, Biondi-Zoccai G, Greco M, Greco T, Frati G, et al. A meta-analysis of complications and mortality of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Crit Care Resusc J Aust Acad Crit Care Med. 2013;15(3):172–178. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical