Concomitant Carboxylate and Oxalate Formation From the Activation of CO2 by a Thorium(III) Complex
- PMID: 27714966
- PMCID: PMC5215673
- DOI: 10.1002/chem.201604622
Concomitant Carboxylate and Oxalate Formation From the Activation of CO2 by a Thorium(III) Complex
Abstract
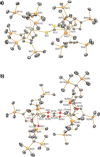
Improving our comprehension of diverse CO2 activation pathways is of vital importance for the widespread future utilization of this abundant greenhouse gas. CO2 activation by uranium(III) complexes is now relatively well understood, with oxo/carbonate formation predominating as CO2 is readily reduced to CO, but isolated thorium(III) CO2 activation is unprecedented. We show that the thorium(III) complex, [Th(Cp'')3 ] (1, Cp''={C5 H3 (SiMe3 )2 -1,3}), reacts with CO2 to give the mixed oxalate-carboxylate thorium(IV) complex [{Th(Cp'')2 [κ2 -O2 C{C5 H3 -3,3'-(SiMe3 )2 }]}2 (μ-κ2 :κ2 -C2 O4 )] (3). The concomitant formation of oxalate and carboxylate is unique for CO2 activation, as in previous examples either reduction or insertion is favored to yield a single product. Therefore, thorium(III) CO2 activation can differ from better understood uranium(III) chemistry.
Keywords: actinides; reduction; small molecule activation; subvalent compounds; thorium.
© 2016 The Authors. Published by Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA.
Figures


References
-
- Falkowski P., Scholes R. J., Boyle E., Canadell J., Canfield D., Elser J., Gruber N., Hibbard K., Hogberg P., Linder S., Mackenzie F. T., B. Moore III , Pedersen T., Rosenthal Y., Seitzinger S., Smetacek V., Steffen W., Science 2000, 290, 291–296. - PubMed
-
- None
-
- Sakakura T., Choi J.-C., Yasuda H., Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2365–2387; - PubMed
-
- Liu Q., Wu L., Jackstell R., Beller M., Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 5933. - PubMed
-
- West N. M., Miller A. J., Labinger J. A., Bercaw J. E., Coord. Chem. Rev. 2001, 255, 881–898.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

