Clinical and paraclinical profile, and predictors of outcome in 90 cases of scrub typhus, Meghalaya, India
- PMID: 27716337
- PMCID: PMC5051022
- DOI: 10.1186/s40249-016-0186-x
Clinical and paraclinical profile, and predictors of outcome in 90 cases of scrub typhus, Meghalaya, India
Abstract
Background: India is an integral component of "tsutsugamushi triangle" which depicts a part of the globe endemic to scrub typhus. Owing to frequent outbreaks witnessed in different parts of the country in the recent past, scrub typhus is described as a re-emerging infectious disease in India. The present study aimed to study the clinical and paraclinical profile, complications and predictors of outcome among 90 cases of scrub typhus diagnosed in a hospital of north-eastern India from Sept 2011 to Aug 2012.
Methods: A longitudinal study was conducted in a hospital of Meghalaya, India between Sept 2011 and Aug 2012. Diagnosis of scrub typhus was arrived by SD BIOLINE tsutsugamushi (solid phase immunochromatographic assay) rapid diagnostic test for antibodies (IgM, IgG or IgA). Descriptive analyses of age, gender, geographic area, symptoms and signs, treatment, laboratory findings, complications, and outcome were conducted. Relative risk (RR) with 95 % confidence interval (CI) was computed for Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome (MODS) and mortality. Binary logistic regression was applied to the significant correlates (P < 0.05) on univariate analysis to identify the predictors of MODS and mortality in scrub typhus.
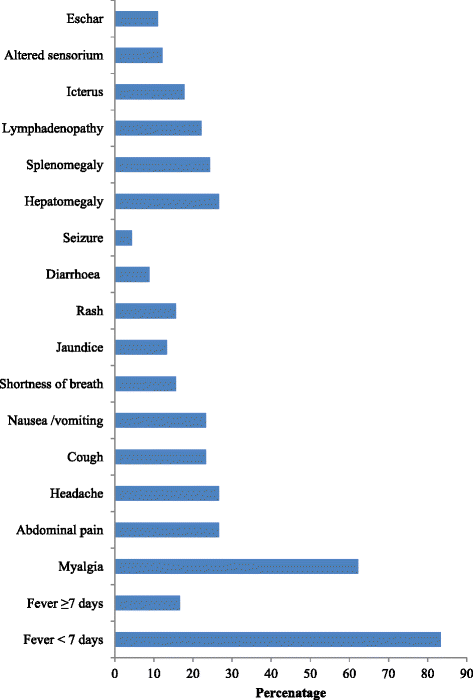
Results: As many as 662 clinically suspected scrub typhus patients were tested and 90 (13.6 %) were diagnosed to have scrub typhus. Out of 90 patients, 52.2 % (n = 47) were males and their mean (SD) age was 36.29 (13.38) years. Fever of <7 days (n = 75, 83.3 %), myalgia (n = 56, 62.2 %), pain abdomen (n = 24, 26.7 %), headache (n = 24, 26.7 %), nausea/vomiting (n = 21, 23.3 %), dry cough (n = 21, 23.3 %), hepatomegaly (n = 24, 26.7 %), splenomegaly (n = 22, 24.4 %), and lymphadenopathy (n = 20, 22.2 %) were the predominant clinical features. Eschar was seen in 10 patients (11.1 %). One third (n = 30) of the patients developed at least one systemic complication. Acute hepatitis (n = 15, 16.7 %), pneumonitis (n = 14, 15.6 %), and acute kidney injury (n = 11, 12.2 %) were the common complications. MODS was seen in 14.4 % (n = 13) and 38.5 % (n = 5) of the patients with MODS died. Overall, case fatality rate was 5.15 % (n = 5). On univariate analysis, platelets <100 000/mm3, serum creatinine >1.5 mg/dl, and transaminase (AST, ALT or both) >500 U/L were associated with MODS (P < 0.001) and mortality (P < 0.05). In addition, serum bilirubin >3 mg/dl was also associated with MODS (P < 0.001). On applying binary logistic regression, serum creatinine >1.5 mg/dl was a predictor of MODS (OR: 76.1, 95 % CI: 4.9-1175.6) and mortality (OR: 18.03, 95 % CI: 1.38-235.1).
Conclusion: In this study setting, approximately one-seventh (13.6 %) of the acute undifferentiated febrile illness were due to scrub typhus. Systemic complications were common (33.3 %). Serum creatinine >1.5 mg/dl was a predictor of MODS and mortality.
Keywords: Hospital; India; Longitudinal; Mortality; Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome (MODS); Scrub typhus.
Figures
References
-
- Ogawa M, Hagiwara T, Kishimoto T, Shiga S, Yoshida Y, Furuya Y, et al. Scrub typhus in Japan: epidemiology and clinical features of cases reported in 1998. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2002;67:162–165. - PubMed
-
- Padbidri VS, Gupta NP. Rickettsiosis in India: A review. J Indian Med Assoc. 1978;71(4):104–107. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous