Preoperative plasma growth-differentiation factor-15 for prediction of acute kidney injury in patients undergoing cardiac surgery
- PMID: 27717384
- PMCID: PMC5055664
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-016-1482-3
Preoperative plasma growth-differentiation factor-15 for prediction of acute kidney injury in patients undergoing cardiac surgery
Abstract
Background: Growth-differentiation factor-15 (GDF-15) is an emerging humoral marker for risk stratification in cardiovascular disease. Cardiac-surgery-associated acute kidney injury (CSA-AKI), an important complication in patients undergoing cardiac surgery, is associated with poor prognosis. The present secondary analysis of an observational cohort study aimed to determine the role of GDF-15 in predicting CSA-AKI compared with the Cleveland-Clinic Acute Renal Failure (CC-ARF) score and a logistic regression model including variables associated with renal dysfunction.
Methods: Preoperative plasma GDF-15 was determined in 1176 consecutive patients undergoing elective cardiac surgery. Patients with chronic kidney disease stage 5 were excluded. AKI was defined according to Kidney-Disease-Improving-Global-Outcomes (KDIGO) - creatinine criteria. The following variables were screened for association with development of postoperative AKI: age, gender, additive Euroscore, serum creatinine, duration of cardiopulmonary bypass, duration of surgery, type of surgery, total circulatory arrest, preoperative hemoglobin, preoperative oxygen-supplemented cerebral oxygen saturation, diabetes mellitus, hemofiltration during ECC, plasma GDF-15, high sensitivity troponin T (hsTNT), and N-terminal prohormone of B-type natriuretic peptide (NTproBNP).
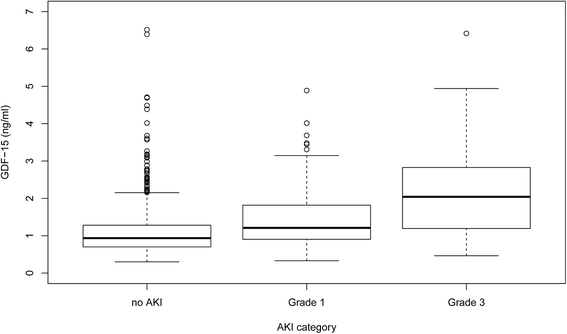
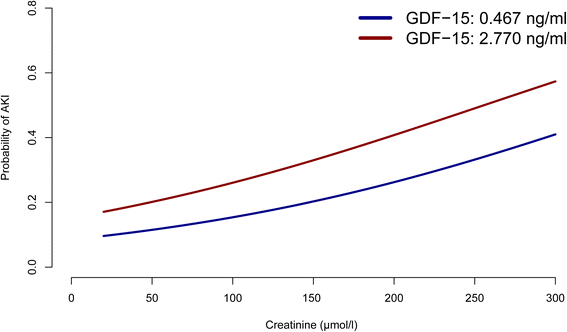
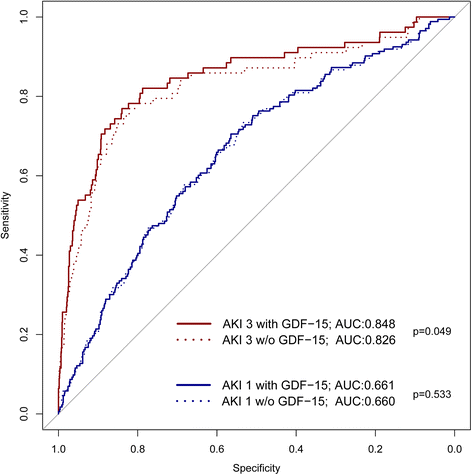
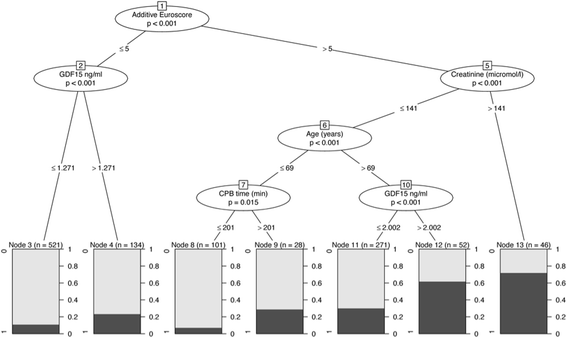
Results: There were 258 patients (21.9 %) with AKI (AKI stage 1 (AKI-1), n = 175 (14.9 %); AKI-2, n = 6 (0.5 %); AKI-3, n = 77 (6.5 %)). The incidence of AKI-1 and AKI-3 increased significantly from the lowest to the highest tertiles of GDF-15. In logistic regression, preoperative GDF-15, additive Euroscore, age, plasma creatinine, diabetes mellitus, and duration of cardiopulmonary bypass were independently associated with AKI. Inclusion of GDF-15 in a logistic regression model comprising these variables significantly increased the area under the curve (AUC 0.738 without and 0.750 with GDF-15 included) and the net reclassification ability to predict AKI. Comparably, in receiver operating characteristic analysis the predictive capacity of the CC-ARF score (AUC 0.628) was improved by adding GDF-15 (AUC 0.684) but this score also had lower predictability than the logistic regression model. In random forest analyses the predictive capacity of GDF-15 was especially pronounced in patients with normal plasma creatinine.
Conclusion: This suggests that preoperative plasma GDF-15 independently predicts postoperative AKI in patients undergoing elective cardiac surgery and is particularly helpful for risk stratification in patients with normal creatinine.
Trial registration: NCT01166360 on July 20, 2010.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Biomarkers; Cardiac surgery; Cleveland Clinic Acute Renal Failure score; Euroscore; Growth-differentiation factor-15.
Figures

Comment in
-
Assessing preoperative plasma growth-differentiation factor-15 for prediction of acute kidney injury in patients undergoing cardiac surgery.Crit Care. 2017 Mar 17;21(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s13054-017-1623-3. Crit Care. 2017. PMID: 28302180 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Heringlake M, Knappe M, Vargas Hein O, Lufft H, Kindgen-Milles D, Böttiger BW, Weigand MR, Klaus S, Schirmer U. Renal dysfunction according to the ADQI-RIFLE system and clinical practice patterns after cardiac surgery in Germany. Minerva Anestesiol. 2006;72:645–54. - PubMed
-
- Pistolesi V, Di Napoli A, Fiaccadori E, Zeppilli L, Sacco MI, Regolisti G, Tritapepe L, Pierucci A, Morabito S. Severe acute kidney injury following cardiac surgery: short-term outcomes in patients undergoing continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) J Nephrol. 2016;29:229–39. doi: 10.1007/s40620-015-0213-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schetz M, Bove T, Morelli A, Mankad S, Ronco C, Kellum JA. Prevention of cardiac surgery-associated acute kidney injury. Int J Artif Organs. 2008;31:179–89. - PubMed
-
- Bellomo R, Auriemma S, Fabbri A, D'Onofrio A, Katz N, McCullough PA, Ricci Z, Shaw A, Ronco C. The pathophysiology of cardiac surgery-associated acute kidney injury (CSA-AKI) Int J Artif Organs. 2008;31:166–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

