Newborn screening for mucopolysaccharidoses: a pilot study of measurement of glycosaminoglycans by tandem mass spectrometry
- PMID: 27718145
- PMCID: PMC5203965
- DOI: 10.1007/s10545-016-9981-6
Newborn screening for mucopolysaccharidoses: a pilot study of measurement of glycosaminoglycans by tandem mass spectrometry
Abstract
Background: Mucopolysaccharidoses (MPS) are a group of inborn errors of metabolism that are progressive and usually result in irreversible skeletal, visceral, and/or brain damage, highlighting a need for early diagnosis.
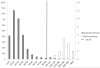
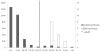
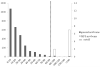
Methods: This pilot study analyzed 2862 dried blood spots (DBS) from newborns and 14 DBS from newborn patients with MPS (MPS I, n = 7; MPS II, n = 2; MPS III, n = 5). Disaccharides were produced from polymer GAGs by digestion with chondroitinase B, heparitinase, and keratanase II. Heparan sulfate (0S, NS), dermatan sulfate (DS) and mono- and di-sulfated KS were measured by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Median absolute deviation (MAD) was used to determine cutoffs to distinguish patients from controls. Cutoffs were defined as median + 7× MAD from general newborns.
Results: The cutoffs were as follows: HS-0S > 90 ng/mL; HS-NS > 23 ng/mL, DS > 88 ng/mL; mono-sulfated KS > 445 ng/mL; di-sulfated KS > 89 ng/mL and ratio di-KS in total KS > 32 %. All MPS I and II samples were above the cutoffs for HS-0S, HS-NS, and DS, and all MPS III samples were above cutoffs for HS-0S and HS-NS. The rate of false positives for MPS I and II was 0.03 % based on a combination of HS-0S, HS-NS, and DS, and for MPS III was 0.9 % based upon a combination of HS-0S and HS-NS.
Conclusions: Combination of levels of two or more different GAGs improves separation of MPS patients from unaffected controls, indicating that GAG measurements are potentially valuable biomarkers for newborn screening for MPS.
Figures
References
-
- Auclair D, Hopwood JJ, Brooks DA, et al. Replacement therapy in Mucopolysaccharidosis type VI: advantages of early onset of therapy. MGM. 2003;78:163–74. - PubMed
-
- Baldo G, Matte U, Artigalas O, et al. Placenta analysis of prenatally diagnosed patients reveals early GAG storage in mucopolysaccharidoses II and VI. MGM. 2011;103:197–8. - PubMed
-
- Baldo G, Mayer FQ, Martinelli BZ, et al. Enzyme replacement therapy started at birth improves outcome in difficult-to-treat organs in mucopolysaccharidosis I mice. MGM. 2013;109:33–40. - PubMed
-
- Beck M, Braun S, Coerdt W, et al. Fetal presentation of Morquio disease type A. Prenat Diagn. 1992;12:1019–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

