SONAR Discovers RNA-Binding Proteins from Analysis of Large-Scale Protein-Protein Interactomes
- PMID: 27720645
- PMCID: PMC5074894
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.09.003
SONAR Discovers RNA-Binding Proteins from Analysis of Large-Scale Protein-Protein Interactomes
Abstract
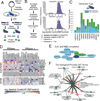
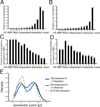
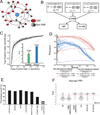
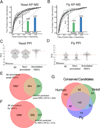
RNA metabolism is controlled by an expanding, yet incomplete, catalog of RNA-binding proteins (RBPs), many of which lack characterized RNA binding domains. Approaches to expand the RBP repertoire to discover non-canonical RBPs are currently needed. Here, HaloTag fusion pull down of 12 nuclear and cytoplasmic RBPs followed by quantitative mass spectrometry (MS) demonstrates that proteins interacting with multiple RBPs in an RNA-dependent manner are enriched for RBPs. This motivated SONAR, a computational approach that predicts RNA binding activity by analyzing large-scale affinity precipitation-MS protein-protein interactomes. Without relying on sequence or structure information, SONAR identifies 1,923 human, 489 fly, and 745 yeast RBPs, including over 100 human candidate RBPs that contain zinc finger domains. Enhanced CLIP confirms RNA binding activity and identifies transcriptome-wide RNA binding sites for SONAR-predicted RBPs, revealing unexpected RNA binding activity for disease-relevant proteins and DNA binding proteins.
Keywords: RNA-binding proteins; machine-learning; protein-protein interaction networks; support vector machine.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Baltz AG, Munschauer M, Schwanhausser B, Vasile A, Murakawa Y, Schueler M, Youngs N, Penfold-Brown D, Drew K, Milek M, et al. The mRNA-bound proteome and its global occupancy profile on protein-coding transcripts. Molecular cell. 2012;46:674–690. - PubMed
-
- Castello A, Fischer B, Eichelbaum K, Horos R, Beckmann BM, Strein C, Davey NE, Humphreys DT, Preiss T, Steinmetz LM, et al. Insights into RNA biology from an atlas of mammalian mRNA-binding proteins. Cell. 2012;149:1393–1406. - PubMed
-
- Castello A, Fischer B, Hentze MW, Preiss T. RNA-binding proteins in Mendelian disease. Trends in genetics : TIG. 2013;29:318–327. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

