Mechanisms, Management, and Treatment of Fibrosis in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
- PMID: 27720839
- PMCID: PMC5209279
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.09.047
Mechanisms, Management, and Treatment of Fibrosis in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
Abstract
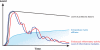
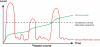
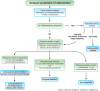
In the last 10 years, we have learned much about the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management of intestinal fibrosis in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases. Just a decade ago, intestinal strictures were considered to be an inevitable consequence of long-term inflammation in patients who did not respond to anti-inflammatory therapies. Inflammatory bowel diseases-associated fibrosis was seen as an irreversible process that frequently led to intestinal obstructions requiring surgical intervention. This paradigm has changed rapidly, due to the antifibrotic approaches that may become available. We review the mechanisms and diagnosis of this serious complication of inflammatory bowel diseases, as well as factors that predict its progression and management strategies.
Keywords: Crohn’s Disease; Dilation; Treatment; Ulcerative Colitis.
Copyright © 2017 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Jeuring S, Van den Heuvel T, Zeegers M, et al. Disease Behavior in Crohn's Disease Patients Diagnosed in the Biological Era - A Dutch Population-Based IBD-SL Cohort Study. Gastroenterology. 2015;148:S22–23.
-
- Pittet V, Rogler G, Michetti P, et al. Penetrating or stricturing diseases are the major determinants of time to first and repeat resection surgery in Crohn's disease. Digestion. 2013;87:212–21. - PubMed
-
- Latella G, Di Gregorio J, Flati V, et al. Mechanisms of initiation and progression of intestinal fibrosis in IBD. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2015;50:53–65. - PubMed
-
- Rieder F, Karrasch T, Ben-Horin S, et al. Results of the 2nd scientific workshop of the ECCO (III): basic mechanisms of intestinal healing. J Crohns Colitis. 2012;6:373–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

