EAF2 regulates DNA repair through Ku70/Ku80 in the prostate
- PMID: 27721405
- PMCID: PMC5386836
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2016.373
EAF2 regulates DNA repair through Ku70/Ku80 in the prostate
Abstract
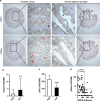
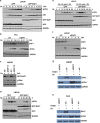
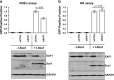
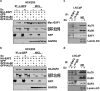
Androgens are known to protect prostate cancer cells from DNA damage. Recent studies showed regulation of DNA repair genes by androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancers. ELL-associated factor 2 (EAF2) is an androgen-regulated tumor suppressor and its intracellular localization can be modulated by ultraviolet light, suggesting a potential role for EAF2 in androgen regulation of DNA repair in prostate cancer cells. Here we show that knockdown of EAF2 or its homolog EAF1 sensitized prostate cancer cells to DNA damage and the sensitization did not require p53. EAF2 knockout mouse prostate was also sensitized to γ-irradiation. Furthermore, EAF2 knockdown blocked androgen repression of LNCaP or C4-2 cells from doxorubicin induction of γH2ax, a DNA damage marker. In human prostate cancer specimens, EAF2 expression was inversely correlated with the level of γH2ax. Further analysis showed that EAF2 and EAF1 are required for the recruitment and retention of Ku70/Ku80 to DNA damage sites and play a functional role in nonhomologous end-joining DNA repair. These findings provide evidence for EAF2 as a key factor mediating androgen protection of DNA damage via Ku70/Ku80 in prostate cancer cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin 2013; 63: 11–30. - PubMed
-
- Bolla M, Van Tienhoven G, Warde P, Dubois JB, Mirimanoff RO, Storme G et al. External irradiation with or without long-term androgen suppression for prostate cancer with high metastatic risk: 10-year results of an EORTC randomised study. Lancet Oncol 2010; 11: 1066–1073. - PubMed
-
- Koontz BF, Lee WR. External beam radiation therapy for clinically localized prostate cancer: when and how we optimize with concurrent hormonal deprivation. Arch Esp Urol 2011; 64: 858–864. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

