Treponema pallidum, the syphilis spirochete: making a living as a stealth pathogen
- PMID: 27721440
- PMCID: PMC5106329
- DOI: 10.1038/nrmicro.2016.141
Treponema pallidum, the syphilis spirochete: making a living as a stealth pathogen
Abstract
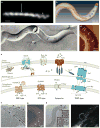
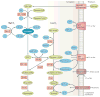
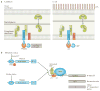
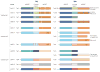
The past two decades have seen a worldwide resurgence in infections caused by Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum, the syphilis spirochete. The well-recognized capacity of the syphilis spirochete for early dissemination and immune evasion has earned it the designation 'the stealth pathogen'. Despite the many hurdles to studying syphilis pathogenesis, most notably the inability to culture and to genetically manipulate T. pallidum, in recent years, considerable progress has been made in elucidating the structural, physiological, and regulatory facets of T. pallidum pathogenicity. In this Review, we integrate this eclectic body of information to garner fresh insights into the highly successful parasitic lifestyles of the syphilis spirochete and related pathogenic treponemes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sena AC, Pillay A, Cox DL, Radolf JD. In: Manual of Clinical Microbiology. Jorgensen JH, et al., editors. ASM Press; Washington, D.C: 2015. pp. 1055–1081.
-
- Smajs D, Norris SJ, Weinstock GM. Genetic diversity in Treponema pallidum: implications for pathogenesis, evolution and molecular diagnostics of syphilis and yaws. Infect Genet Evol. 2012;12:191–202. This is a comprehensive review of the genetic and evolutionary relatioships among pathogenic treponemes based on genomic sequencing data. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

