Timely antiretroviral prophylaxis during pregnancy effectively reduces HIV mother-to-child transmission in eight counties in China: a prospective study during 2004-2011
- PMID: 27721453
- PMCID: PMC5056360
- DOI: 10.1038/srep34526
Timely antiretroviral prophylaxis during pregnancy effectively reduces HIV mother-to-child transmission in eight counties in China: a prospective study during 2004-2011
Abstract
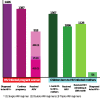
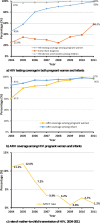
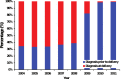
This study investigates the improvement of the prevention of mother-to-child transmission (PMTCT) of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) in China during 2004-2011. A clinic-based prospective study was conducted among HIV-positive pregnant women and their children in eight counties across China. Associated factors of mother-to-child transmission were analyzed using regression analysis. A total of 1,387 HIV+ pregnant women and 1,377 HIV-exposed infants were enrolled. The proportion of pregnant women who received HIV testing increased significantly from 45.1% to 98.9% during 2004-2011. Among whom, the proportion that received antiretroviral (ARV) prophylaxis increased from 61% to 96%, and the corresponding coverage in children increased from 85% to 97% during the same period. In contrast, single-dose nevirapine treatment during delivery declined substantially from 97.9% to 12.7%. Vertical transmission of HIV declined from 11.1% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 5.7-23.3%) in 2004 to 1.2% (95% CI: 0.1-5.8%) in 2011. Women who had a vaginal delivery (compared to emergency caesarian section (odds ratio [OR] = 0.46; 0.23-0.96)) and mothers on multi-ARVs (OR = 0.11; 0.04-0.29) were less likely to transmit HIV to their newborns. Increasing HIV screening enabled timely HIV care and prophylaxis to reduce vertical transmission of HIV. Early and consistent treatment with multi-ARVs during pregnancy is vital for PMTCT.
Figures
References
-
- WHO. Global update on the health sector response to HIV (2014) Available at: http://www. who.int/hiv/pub/mtct/strategic_vision/en/ (Accessed: July 2014).
-
- WHO, UNAIDS and UNICEF. Progress report 2011: Global HIV/AIDS response: Epidemic update and health sector progress towards Universal Access, Progress Report. (2011) Available at: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/44787/1/9789241502986_eng.pdf/ (Accessed: 31 November 2011).
-
- WHO. PMTCT strategic vision 2010–2015: Preventing mother-to child transmission of HIV to reach the UNGASS and Millennium Development Goals. (2010) Available at: http://www.who.int/hiv/pub/mtct/strategic_vision/en/ (Accessed: 2 February 2010).
-
- WHO and UNICEF with the Inter-Agency Task Team. Guidance on global scale-up of the prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV: towards universal access for women, infants and young children and eliminating HIV and AIDS among children. Geneva: WHO. (2007) Available at: http://www.unicef.org/aids/files/PMTCT_enWEBNov26.pdf (Accessed:11 April 2015).
-
- De Cock K. M. et al.. Prevention of mother-to-child HIV transmission in resource-poor countries: translating research into policy and practice. JAMA. 283, 1175–1182 (2000). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

