Bilateral elongated mandibular coronoid process in an Anatolian skull
- PMID: 27722017
- PMCID: PMC5052233
- DOI: 10.5115/acb.2016.49.3.217
Bilateral elongated mandibular coronoid process in an Anatolian skull
Abstract
Elongation or hyperplasia of coronoid process of mandible is rare condition characterized by abnormal bone development which cause malocclusion and the limited mouth opening. In this study, in an Anatolian skull, a case of bilateral elongation of mandibular coronoid process was presented. Levandoski panographic analysis was performed on the panoramic radiographie to determine the hyperplasia of the coronoid process. The right condylar process was exactly hyperplastic. The measurements of Kr-Go/Cd-Go were 95.10 mm/79.03 mm on right side and 97.53 mm/87.80 mm on left side. The ratio of Kr-Go/Cd-Go on the right side was 1.20. Elongated coronoid process is one of the factors cause mandibular hypomobility, it as reported here might lead to limited mouth opening. The knowledge of this variation or abnormality can be useful for the radiologist and surgeons and prevent misdiagnosis.
Keywords: Coronoid process hyperplasia; Elongated coronoid process; Embryology; Mandible; Panoramic radiograph.
Figures
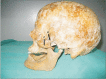
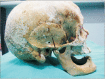
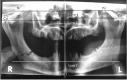
References
-
- Standring S. Gray's anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice. 40th ed. Edinburg: Churchill & Livingstone; 2008. pp. 530–532.
-
- Hönig JF, Merten HA, Halling F, Korth OE. An X-ray study of the incidence of asymptomatic hypertrophy of the coronoid process. Schweiz Monatsschr Zahnmed. 1993;103:281–284. - PubMed
-
- Lucaya J, Herrera M, Vera J. Unilateral hyperplasia of the coronoid process in a child: a cause of restricted opening of the mouth. Radiology. 1982;144:528. - PubMed
-
- Mulder CH, Kalaykova SI, Gortzak RA. Coronoid process hyperplasia: a systematic review of the literature from 1995. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012;41:1483–1489. - PubMed
-
- Pregarz M, Fugazzola C, Consolo U, Andreis IA, Beltramello A, Gotte P. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging in the management of coronoid process hyperplasia: review of five cases. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 1998;27:215–220. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
