Corchorus Olitorius Linn: A Rich Source of Ω3-Fatty Acids
- PMID: 27722021
- PMCID: PMC5053770
- DOI: 10.4172/2153-2435.1000486
Corchorus Olitorius Linn: A Rich Source of Ω3-Fatty Acids
Abstract
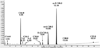
Fatty acids composition of Corchorus olitorius Linn were identified as their methyl esters using accurate mass gas chromatography quadrupole time of flight mass spectrometry (GCQTOF) in chemical ionization (CI) and electron ionization (EI) modes. The leaves which are the edible part of the plant were found to be very rich in ω3-octadecatriene fatty acid reaching up to more than 49 % of the total fatty acids contents. This is the first report to unequivocally detect ω-3 fatty acid in Corchorus olitorius Linn with a much higher concentration than any other reported vegetable and further investigation into its health effects are clearly warranted.
Keywords: Chemical ionization; Electron ionization; FAMES; Fatty acids methyl esters; GCQTOF; Molokhia.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Fatty acids composition of Caenorhabditis elegans using accurate mass GCMS-QTOF.J Environ Sci Health B. 2016 Aug 2;51(8):546-52. doi: 10.1080/03601234.2016.1170555. Epub 2016 May 11. J Environ Sci Health B. 2016. PMID: 27166662 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of very long-chain (>C24) fatty acid methyl esters using gas chromatography coupled to quadrupole/time-of-flight mass spectrometry with atmospheric pressure chemical ionization source.Anal Chim Acta. 2019 Mar 21;1051:103-109. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2018.11.001. Epub 2018 Nov 5. Anal Chim Acta. 2019. PMID: 30661606
-
Antimicrobial Bioactivity and GC-MS Analysis of Different Extracts of Corchorus olitorius L Leaves.ScientificWorldJournal. 2022 Sep 20;2022:3382302. doi: 10.1155/2022/3382302. eCollection 2022. ScientificWorldJournal. 2022. PMID: 36177438 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological and phytochemical biodiversity of Corchorus olitorius.RSC Adv. 2022 Dec 7;12(54):35103-35114. doi: 10.1039/d2ra07406k. eCollection 2022 Dec 6. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 36540263 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nutritional composition of molokhia (Corchorus olitorius) and stamnagathi (Cichorium spinosum).World Rev Nutr Diet. 2003;91:1-21. doi: 10.1159/000069924. World Rev Nutr Diet. 2003. PMID: 12747085 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
A Comprehensive Review of C. capsularis and C. olitorius: A Source of Nutrition, Essential Phytoconstituents and Pharmacological Activities.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jul 12;11(7):1358. doi: 10.3390/antiox11071358. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35883849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phytochemical Screening and Antimicrobial Activity Evaluation of Selected Medicinal Plants in Ethiopia.J Exp Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 8;15:51-62. doi: 10.2147/JEP.S379805. eCollection 2023. J Exp Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36789235 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bolus L. Flora of Egypt. Vol. 5. Cairo, Egypt: Al Hadara Publishing; 2002. pp. 296–299.
-
- Ali H, Houghton PJ, Soumyanath A. α-Amylase inhibitory activity of some Malaysian plants used to treat diabetes; with particular reference to Phyllanthus amarus. J Ethnopharmacol. 2006;107:449–455. - PubMed
-
- Bennett J, Brown CM. Use of herbal remedies by patients in a health maintenance organization. J Am Pharm Assoc. 2000;40:353–358. - PubMed
-
- Dirks NL, Huth B, Yates CR, Meibohm B. Pharmacokinetics of immunosuppressants: a perspective on ethnic differences. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2004;42:701–718. - PubMed
-
- Foster BC, Vandenhoek S, Hana J, Krantis A, Akhtar MH. In vitro inhibition of human cytochrome P450-mediated metabolism of marker substrates by natural products. Phytomedicine. 2003;10:334–342. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
