An analysis of the global pharmacy workforce capacity
- PMID: 27724966
- PMCID: PMC5057428
- DOI: 10.1186/s12960-016-0158-z
An analysis of the global pharmacy workforce capacity
Abstract
Background: The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that there is a global healthcare workforce shortage of 7.2 million, which is predicted to grow to 12.9 million by 2035. Globally, people are living longer with multiple co-morbidities and require increased access and use of medicines. Pharmacists are a key component of the healthcare workforce, and in many countries, pharmacists are the most accessible healthcare profession. This paper identifies key issues and current trends affecting the global pharmacy workforce, in particular workforce distribution, country economic status, capacity, and workforce gender balance.
Methods: National professional pharmacy leadership bodies, together with other contacts for professional bodies, regulatory bodies, and universities, were approached to provide country-level data on pharmacy workforce. A descriptive and comparative analysis was conducted to assess each country's pharmacy workforce.
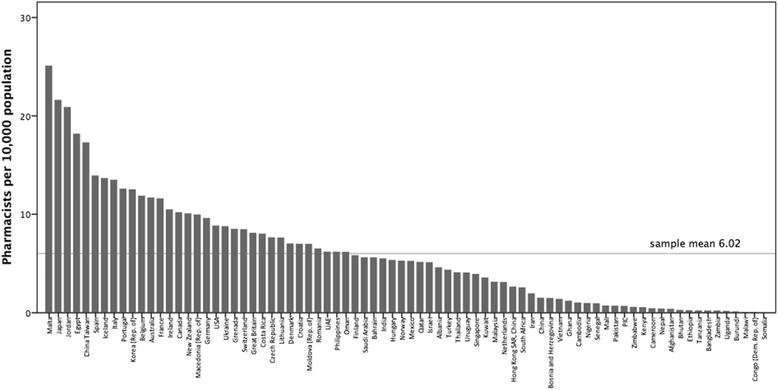
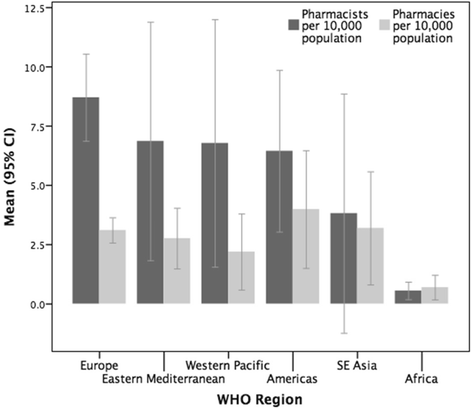
Results: A total of 89 countries and territories responded to the survey. To standardise the capacity measure, an analysis of the population density of pharmacists (per 10 000 population) was performed. The sample mean was 6 pharmacists per 10 000 population (n = 80). There is considerable variation between the surveyed countries/territories ranging from 0.02 (Somalia) to 25.07 (Malta) pharmacists per 10 000 population. African nations have significantly fewer pharmacists per capita. Pharmacist density correlates with gross national income (GNI) and health expenditure. The majority of pharmacists are employed in community settings, followed by hospital, industry-related, academia, and regulation. There is a greater proportion of females in the pharmacy workforce globally, with some WHO regions showing female representation of more than 65 % with an increasing trend trajectory.
Conclusions: Pharmacy workforce capacity varies considerably between countries and regions and generally correlates with population- and country-level economic indicators. Those countries and territories with lower economic indicators tend to have fewer pharmacists and pharmacy technicians; this has implications for inequalities regarding access to medicines and medicine expertise.
Keywords: Capacity; Global; Healthcare; Pharmacy workforce.
Figures



References
-
- Global Health Workforce Alliance . Knowledge centre—a universal truth: no health without a workforce. 2013.
-
- World Health Organization . Health topics—Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) 2000.
-
- World Health Organization . Programmes—world health report 2006. 2006.
-
- World Health Organization . Programmes—world health report 2008 primary health care (now more than ever) 2008.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

