Prognostic Factors Related to Dementia with Lewy Bodies Complicated with Pneumonia: An Autopsy Study
- PMID: 27725535
- PMCID: PMC5088536
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.55.6868
Prognostic Factors Related to Dementia with Lewy Bodies Complicated with Pneumonia: An Autopsy Study
Abstract
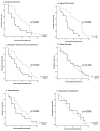
Objective In patients demonstrating dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), pneumonia is a common complication. However, the prognostic factors for the survival time in DLB with pneumonia have not been investigated by autopsy in patients with neuropathologically confirmed DLB. Methods We conducted a retrospective study of the medical and autopsy reports of 42 patients admitted to a Japanese hospital between 2005 and 2014. The patients were neuropathologically diagnosed as having DLB by post-mortem examinations. We analyzed the effects of various factors on the time from DLB onset to death. Results Thirty-nine of the 42 patients with DLB (92.9%) developed pneumonia during hospitalization. The median age at DLB onset was 78 years and the median time from DLB onset to death was 8 years. The Cox proportional hazard model demonstrated cerebral infarction [Hazard Ratio (HR), 2.36 (95% CI 1.12-4.96), p=0.023], muscle weakness [HR, 2.04 (0.95-4.39), p=0.067], male sex [HR, 2.84 (1.24-6.50), p=0.014], and age at onset (≥78 years.) [HR, 4.71 (1.82-12.18), p=0.001] to be prognostic factors for a shorter time from DLB onset to death. Conclusion Careful treatment of cerebral infarction and muscle weakness of the lower extremities is crucial for DLB patients with pneumonia, especially for those over 78 years of age, in order to maximize the patients' life expectancies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Influence of pneumonia complications on the prognosis of patients with autopsy-confirmed Alzheimer's disease, dementia with Lewy bodies, and vascular dementia.Psychogeriatrics. 2016 Sep;16(5):305-14. doi: 10.1111/psyg.12163. Epub 2015 Oct 29. Psychogeriatrics. 2016. PMID: 26510708
-
Concomitant AD pathology affects clinical manifestation and survival in dementia with Lewy bodies.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2017 Feb;88(2):113-118. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2016-313775. Epub 2016 Oct 28. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 27794030
-
Reappraisal of a consecutive autopsy series of patients with primary degenerative dementia: Lewy-related pathology.APMIS. 2007 Jul;115(7):820-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0463.2007.apm_521.x. APMIS. 2007. PMID: 17614849
-
Three years survival in patients with a clinical diagnosis of dementia with Lewy bodies.Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2000 Mar;15(3):267-73. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1099-1166(200003)15:3<267::aid-gps107>3.0.co;2-7. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2000. PMID: 10713586 Review.
-
Dementia with Lewy bodies.Semin Clin Neuropsychiatry. 2003 Jan;8(1):46-57. doi: 10.1053/scnp.2003.50006. Semin Clin Neuropsychiatry. 2003. PMID: 12567332 Review.
Cited by
-
Pneumonia-associated death in patients with dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2019 Mar 14;14(3):e0213825. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0213825. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30870526 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Brain Regional Detection, Histopathology, Gene Expression, and Immunomodulatory Changes in Decedents with COVID-19.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2022 Aug 16;81(9):666-695. doi: 10.1093/jnen/nlac056. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35818336 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Brain Ischemia, Infarction and Hemorrhage in Subjects Dying with or Without Autopsy-Proven Acute Pneumonia.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2021 Mar 26:2021.03.22.21254139. doi: 10.1101/2021.03.22.21254139. medRxiv. 2021. PMID: 33791728 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Relative survival in patients with dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson's disease dementia.PLoS One. 2018 Aug 10;13(8):e0202044. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0202044. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30096198 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic predictors relevant to end-of-life palliative care in Parkinson's disease and related disorders: a systematic review.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2021 Mar 31;92(6):629-36. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2020-323939. Online ahead of print. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33789923 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- McKeith IG, Galasko D, Kosaka K, et al. . Consensus guidelines for the clinical and pathologic diagnosis of dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB): report of the consortium on DLB international workshop. Neurology 47: 1113-1124, 1996. - PubMed
-
- Kosaka K, Yoshimura M, Ikeda K, Budka H. Diffuse type of Lewy body disease: progressive dementia with abundant cortical Lewy bodies and senile changes of varying degree-a new disease? Clin Neuropathol 3: 185-192, 1984. - PubMed
-
- Perry RH, Irving D, Blessed G, Fairbairn A, Perry EK. Senile dementia of Lewy body type. A clinically and neuropathologically distinct form of Lewy body dementia in the elderly. J Neurol Sci 95: 119-139, 1990. - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto T, Kobayashi Y, Murata M. Risk of pneumonia onset and discontinuation of oral intake following videofluorography in patients with Lewy body disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 16: 503-506, 2010. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical