Alternative genetic mechanisms of BRAF activation in Langerhans cell histiocytosis
- PMID: 27729324
- PMCID: PMC5123197
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2016-08-733790
Alternative genetic mechanisms of BRAF activation in Langerhans cell histiocytosis
Abstract
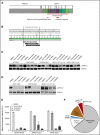
Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) is characterized by inflammatory lesions containing pathologic CD207+ dendritic cells with constitutively activated ERK. Mutually exclusive somatic mutations in MAPK pathway genes have been identified in ∼75% of LCH cases, including recurrent BRAF-V600E and MAP2K1 mutations. To elucidate mechanisms of ERK activation in the remaining 25% of patients, we performed whole-exome sequencing (WES, n = 6), targeted BRAF sequencing (n = 19), and/or whole-transcriptome sequencing (RNA-seq, n = 6) on 24 LCH patient samples lacking BRAF-V600E or MAP2K1 mutations. WES and BRAF sequencing identified in-frame BRAF deletions in the β3-αC loop in 6 lesions. RNA-seq revealed one case with an in-frame FAM73A-BRAF fusion lacking the BRAF autoinhibitory regulatory domain but retaining an intact kinase domain. High levels of phospho-ERK were detected in vitro in cells overexpressing either BRAF fusion or deletion constructs and ex vivo in CD207+ cells from lesions. ERK activation was resistant to BRAF-V600E inhibition, but responsive to both a second-generation BRAF inhibitor and a MEK inhibitor. These results support an emerging model of universal ERK-activating genetic alterations driving pathogenesis in LCH. A personalized approach in which patient-specific alterations are identified may be necessary to maximize benefit from targeted therapies for patients with LCH.
© 2016 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures
References
-
- Allen CE, Parsons DW. Biological and clinical significance of somatic mutations in Langerhans cell histiocytosis and related histiocytic neoplastic disorders. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2015;2015:559-564. - PubMed
-
- Nelson DS, Quispel W, Badalian-Very G, et al. Somatic activating ARAF mutations in Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Blood. 2014;123(20):3152-3155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

