Backtracked and paused transcription initiation intermediate of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase
- PMID: 27729537
- PMCID: PMC5087071
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1605038113
Backtracked and paused transcription initiation intermediate of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase
Abstract
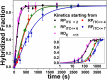
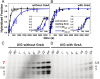
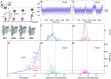
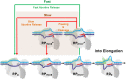
Initiation is a highly regulated, rate-limiting step in transcription. We used a series of approaches to examine the kinetics of RNA polymerase (RNAP) transcription initiation in greater detail. Quenched kinetics assays, in combination with gel-based assays, showed that RNAP exit kinetics from complexes stalled at later stages of initiation (e.g., from a 7-base transcript) were markedly slower than from earlier stages (e.g., from a 2- or 4-base transcript). In addition, the RNAP-GreA endonuclease accelerated transcription kinetics from otherwise delayed initiation states. Further examination with magnetic tweezers transcription experiments showed that RNAP adopted a long-lived backtracked state during initiation and that the paused-backtracked initiation intermediate was populated abundantly at physiologically relevant nucleoside triphosphate (NTP) concentrations. The paused intermediate population was further increased when the NTP concentration was decreased and/or when an imbalance in NTP concentration was introduced (situations that mimic stress). Our results confirm the existence of a previously hypothesized paused and backtracked RNAP initiation intermediate and suggest it is biologically relevant; furthermore, such intermediates could be exploited for therapeutic purposes and may reflect a conserved state among paused, initiating eukaryotic RNA polymerase II enzymes.
Keywords: RNA polymerase; RNAP; backtracking; pausing; transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Murakami KS, Darst SA. Bacterial RNA polymerases: The wholo story. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2003;13(1):31–39. - PubMed
-
- Young BA, Gruber TM, Gross CA. Views of transcription initiation. Cell. 2002;109(4):417–420. - PubMed
-
- Hsu LM. Promoter clearance and escape in prokaryotes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002;1577(2):191–207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

