Scutellaria baicalensis, the golden herb from the garden of Chinese medicinal plants
- PMID: 27730005
- PMCID: PMC5031759
- DOI: 10.1007/s11434-016-1136-5
Scutellaria baicalensis, the golden herb from the garden of Chinese medicinal plants
Abstract
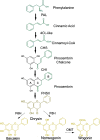
Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, or Chinese skullcap, has been widely used as a medicinal plant in China for thousands of years, where the preparation from its roots is called Huang-Qin. It has been applied in the treatment of diarrhea, dysentery, hypertension, hemorrhaging, insomnia, inflammation and respiratory infections. Flavones such as baicalin, wogonoside and their aglycones baicalein wogonin are the major bioactive compounds extracted from the root of S. baicalensis. These flavones have been reported to have various pharmacological functions, including anti-cancer, hepatoprotection, antibacterial and antiviral, antioxidant, anticonvulsant and neuroprotective effects. In this review, we focus on clinical applications and the pharmacological properties of the medicinal plant and the flavones extracted from it. We also describe biotechnological and metabolic methods that have been used to elucidate the biosynthetic pathways of the bioactive compounds in Scutellaria.
黄芩是一种常用的药用植物, 中国人对它的使用了已有数千年历史。黄芩根的制备物, 为常用的中药材, 在中国传统医学中用来治疗腹泻、痢疾、高血压、出血、 失眠、炎症和呼吸道感染。黄芩根中主要的活性物质为黄酮物质黄芩苷, 汉黄芩苷及 苷元黄芩素, 汉黄芩素。药理学研究显示这些黄酮物质具有多种药物学活性, 包括抗 癌, 保肝、抗菌、抗病毒、抗氧化、抗惊厥和神经系统保护作用。在本综述里面, 我 们集中介绍了黄芩的临床应用及药物学活性。我们也介绍了用于研究黄芩中活性物质 代谢途径的生物技术及代谢生物学方法。.
Keywords: Anti-cancer; Flavonoids; Medicinal plants; Metabolic biology; Scutellaria baicalensis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Li S (1593 and republished in 2012). In: Compendium of materia medica (Bencao Gangmu). Huaxia Press, pp 543–546 (In Chinese)
-
- Xu S (Around 200 AD and republished in 1978) Shuowen Jiezi (Explaining graphs and analyzing characters). Zhonghua Book Company, p 19 (In Chinese)
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

