An Xp11.2 translocation renal cell carcinoma with SMARCB1 (INI1) inactivation in adult end-stage renal disease: a case report
- PMID: 27733182
- PMCID: PMC5062893
- DOI: 10.1186/s13000-016-0551-x
An Xp11.2 translocation renal cell carcinoma with SMARCB1 (INI1) inactivation in adult end-stage renal disease: a case report
Abstract
Background: Xp11.2 translocation/transcription factor E3 (TFE3) rearrangement renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is a rare subtype of RCC with limited clinical and pathological data.
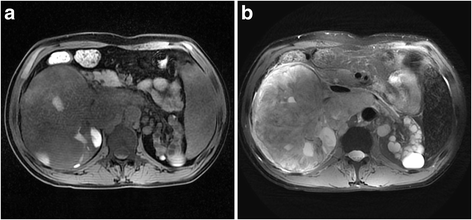
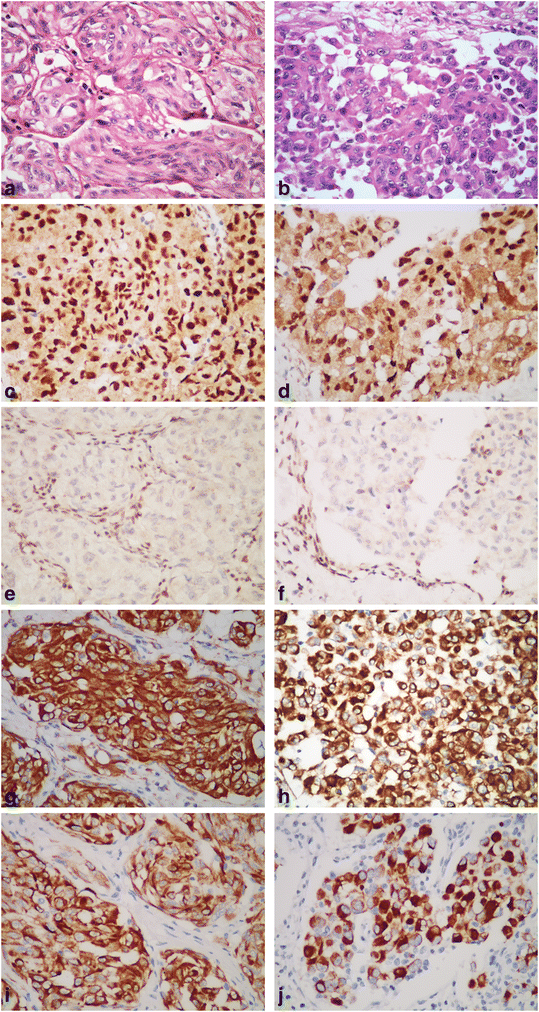
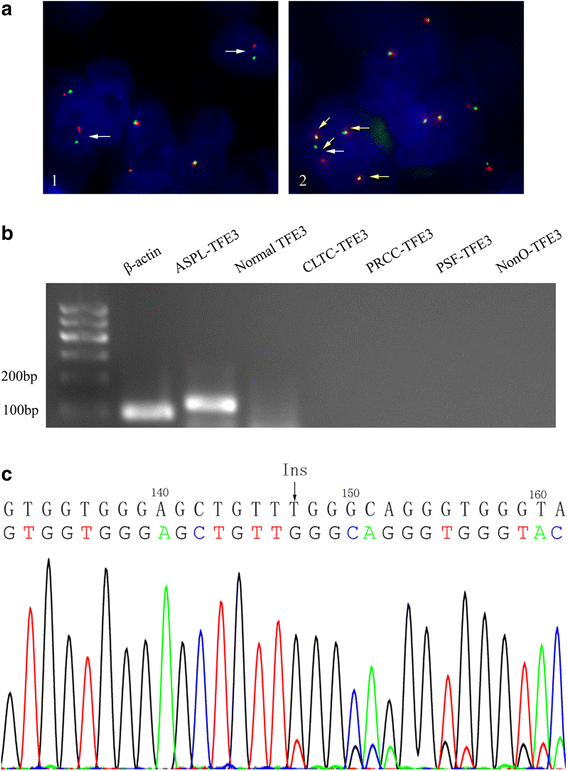
Case presentation: Here we present an unusual high-grade Xp11.2 translocation RCC with a rhabdoid feature and SMARCB1 (INI1) inactivation in a 40-year-old man with end-stage kidney disease. The histological examination of the dissected left renal tumor showed an organoid architecture of the eosinophilic or clear neoplastic cells with necrosis and high mitotic activity. In some areas, non-adhesive tumor cells with eccentric nuclei were observed. Immunohistochemically (IHC), the tumor cells are positive for TFE3 and the renal tubular markers (PAX2 and PAX8), and completely negative for SMARCB1, an oncosuppressor protein. Break-apart florescence in situ hybridization and reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction confirmed TFE3 rearrangement on Xp11.2 and the presence of ASPSCR1-TFE3 fusion gene. DNA sequencing revealed a frameshift mutation in exon 4 of SMARCB1 gene.
Conclusion: It is important to recognize this rare RCC with both TFE3 rearrangement and SMARCB1 inactivation, as the prognosis and therapeutic strategies, particularly targeted therapies for such tumors, might be different.
Keywords: Kidney; Renal cell carcinoma; SMARCB1; TFE3; Xp11.2.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TFE3 break-apart FISH has a higher sensitivity for Xp11.2 translocation-associated renal cell carcinoma compared with TFE3 or cathepsin K immunohistochemical staining alone: expanding the morphologic spectrum.Am J Surg Pathol. 2013 Jun;37(6):804-15. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e31827e17cb. Am J Surg Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23598965
-
PSF/SFPQ is a very common gene fusion partner in TFE3 rearrangement-associated perivascular epithelioid cell tumors (PEComas) and melanotic Xp11 translocation renal cancers: clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and molecular characteristics suggesting classification as a distinct entity.Am J Surg Pathol. 2015 Sep;39(9):1181-96. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000502. Am J Surg Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26274027
-
Utilization of a TFE3 break-apart FISH assay in a renal tumor consultation service.Am J Surg Pathol. 2013 Aug;37(8):1150-63. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e31828a69ae. Am J Surg Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23715164
-
RBM10-TFE3 renal cell carcinoma characterised by paracentric inversion with consistent closely split signals in break-apart fluorescence in-situ hybridisation: study of 10 cases and a literature review.Histopathology. 2019 Aug;75(2):254-265. doi: 10.1111/his.13866. Epub 2019 Jun 25. Histopathology. 2019. PMID: 30908700 Review.
-
ALK rearrangement in TFE3-positive renal cell carcinoma: Alternative diagnostic option to exclude Xp11.2 translocation carcinoma.Pathol Res Pract. 2020 Dec;216(12):153286. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2020.153286. Epub 2020 Nov 9. Pathol Res Pract. 2020. PMID: 33197836 Review.
Cited by
-
Update on Selected High-grade Renal Cell Carcinomas of the Kidney: FH-deficient, ALK-rearranged, and Medullary Carcinomas.Adv Anat Pathol. 2024 Mar 1;31(2):118-125. doi: 10.1097/PAP.0000000000000426. Epub 2023 Dec 25. Adv Anat Pathol. 2024. PMID: 38145398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The WHO 2022 Classification of Renal Neoplasms (5th Edition): Salient Updates.Cureus. 2024 Apr 17;16(4):e58470. doi: 10.7759/cureus.58470. eCollection 2024 Apr. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38765391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MRI Characteristics of Pediatric and Young-Adult Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Single-Center Retrospective Study and Literature Review.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Feb 22;15(5):1401. doi: 10.3390/cancers15051401. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36900194 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

