Dual action of neurokinin-1 antagonists on Mas-related GPCRs
- PMID: 27734033
- PMCID: PMC5053144
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.89362
Dual action of neurokinin-1 antagonists on Mas-related GPCRs
Abstract
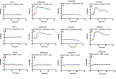
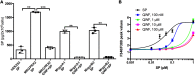
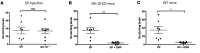
The challenge of translating findings from animal models to the clinic is well known. An example of this challenge is the striking effectiveness of neurokinin-1 receptor (NK-1R) antagonists in mouse models of inflammation coupled with their equally striking failure in clinical investigations in humans. Here, we provide an explanation for this dichotomy: Mas-related GPCRs (Mrgprs) mediate some aspects of inflammation that had been considered mediated by NK-1R. In support of this explanation, we show that conventional NK-1R antagonists have off-target activity on the mouse receptor MrgprB2 but not on the homologous human receptor MRGPRX2. An unrelated tripeptide NK-1R antagonist has dual activity on MRGPRX2. This tripeptide both suppresses itch in mice and inhibits degranulation from the LAD-2 human mast cell line elicited by basic secretagogue activation of MRGPRX2. Antagonists of Mrgprs may fill the void left by the failure of NK-1R antagonists.
Figures



References
-
- Rost K, Fleischer F, Nieber K. [Neurokinin 1 receptor antagonists--between hope and disappointment] Med Monatsschr Pharm. 2006;29(6):200–205. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

