The Influence of Parental Emotional Neglect on Assault Victims Seeking Treatment for Depressed Mood and Alcohol Misuse: A Pilot Study
- PMID: 27735838
- PMCID: PMC5086590
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm5100088
The Influence of Parental Emotional Neglect on Assault Victims Seeking Treatment for Depressed Mood and Alcohol Misuse: A Pilot Study
Abstract
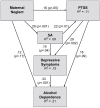
This study explores the relationship between reported parental emotional neglect when a child, assault type experienced, posttraumatic stress symptoms (PTSS), depression, and alcohol consumption in treatment seekers for comorbid depressive symptoms and alcohol misuse. Participants (n = 220) with concurrent depression and alcohol misuse were recruited from the DAISI (Depression and Alcohol Integrated and Single-focussed Interventions) project. Assault type and PTSS were retrospectively assessed by the Posttraumatic Stress Diagnostic Scale. The Measure of Parenting Style is a self-report measure that retrospectively assessed emotional neglect experienced as a child. An exploratory factor analysis using the tetrachoric correlation matrix (applying principal factor extraction with a varimax rotation) identified the two assault factors of sexual assault (SA) and physical assault (PA). A path analysis revealed that Maternal Emotional Neglect increased the impact of PTSS and depression. Paternal Emotional Neglect increased the impact of PA on PTSS and alcohol dependence symptoms. There appears to be differential effects of assault type and Maternal/Paternal emotional neglect on depression and alcohol misuse, suggesting that parenting roles serve distinct protective functions.
Keywords: alcohol misuse; comorbidity and child neglect; depression; trauma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicting interests.
Figures

References
-
- Australian Centre for Posttraumatic Mental Health (ACPMH) Australian Guidelines for the Treatment of Adults with Stress Disorder and Posttraumatic Stress Disorder: Practitioner Guide. [(accessed on 21 September 2016)]. Available online: www.acpmh.unimelb.edu.au.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

