One Binder to Bind Them All
- PMID: 27735880
- PMCID: PMC5087453
- DOI: 10.3390/s16101665
One Binder to Bind Them All
Abstract
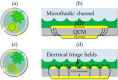
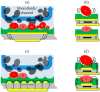
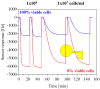
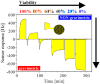
High quality binders, such as antibodies, are of critical importance for chemical sensing applications. With synthetic alternatives, such as molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs), less sensor development time and higher stability of the binder can be achieved. In this feature paper, I will discuss the impact of synthetic binders from an industrial perspective and I will challenge the molecular imprinting community on the next step to leapfrog the current status quo of MIPs for (bio)sensing. Equally important, but often neglected as an effective chemical sensor, is a good match of transducer and MIP coating for a respective application. To demonstrate an application-driven development, a biosensing use case with surface-imprinted layers on piezoacoustic sensors is reported. Depending on the electrode pattern for the transducer, the strong mechanical coupling of the analyte with the MIP layer coated device allows the adoption of the sensitivity from cell mass to cell viability with complete reversibility.
Keywords: aptamers; binder; cells; environment; healthcare; life science; lithography; molecularly imprinted polymers; quartz crystal microbalance; receptor; sensor.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hybrid synthetic receptor composed of molecularly imprinted polydopamine and aptamers for impedimetric biosensing of urea.Mikrochim Acta. 2019 Jan 9;186(2):71. doi: 10.1007/s00604-018-3180-0. Mikrochim Acta. 2019. PMID: 30627876
-
Molecular Imprinting Technology in Quartz Crystal Microbalance (QCM) Sensors.Sensors (Basel). 2017 Feb 24;17(3):454. doi: 10.3390/s17030454. Sensors (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28245588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecularly imprinted polymers for sample preparation and biosensing in food analysis: Progress and perspectives.Biosens Bioelectron. 2017 May 15;91:606-615. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2017.01.018. Epub 2017 Jan 11. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017. PMID: 28103516 Review.
-
[Molecularly imprinted polymers in electro analysis of proteins].Biomed Khim. 2015 May-Jun;61(3):325-31. doi: 10.18097/PBMC20156103325. Biomed Khim. 2015. PMID: 26215409 Review. Russian.
-
Molecular Imprinting with Functional DNA.Small. 2019 Jun;15(26):e1805246. doi: 10.1002/smll.201805246. Epub 2019 Feb 13. Small. 2019. PMID: 30761744 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Point-of-Care Testing for Cardiovascular Disease.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Aug 9;19(16):3485. doi: 10.3390/s19163485. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31395843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Imprinting and Functional Polymers for All Transducers and Applications.Sensors (Basel). 2018 Jan 24;18(2):327. doi: 10.3390/s18020327. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29364150 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rotello V., Thayumanavan S. Molecular Recognition and Polymers: Control of Polymer Structure and Self-Assembly. 1st ed. John Wiley & Sons; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2008.
-
- Sellergren B. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: Man-Made Mimics of Antibodies and their Applications in Analytical Chemistry. 1st ed. Elsevier Science B.V.; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2001.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

