Sequential One-Pot Multienzyme Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of Glycosphingolipid Glycans
- PMID: 27736072
- PMCID: PMC5775905
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.joc.6b01905
Sequential One-Pot Multienzyme Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of Glycosphingolipid Glycans
Abstract
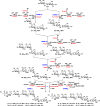
Glycosphingolipids are a diverse family of biologically important glycolipids. In addition to variations on the lipid component, more than 300 glycosphingolipid glycans have been characterized. These glycans are directly involved in various molecular recognition events. Several naturally occurring sialic acid forms have been found in sialic acid-containing glycosphingolipids, namely gangliosides. However, ganglioside glycans containing less common sialic acid forms are currently not available. Herein, highly effective one-pot multienzyme (OPME) systems are used in sequential for high-yield and cost-effective production of glycosphingolipid glycans, including those containing different sialic acid forms such as N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac), N-glycolylneuraminic acid (Neu5Gc), 2-keto-3-deoxy-d-glycero-d-galacto-nononic acid (Kdn), and 8-O-methyl-N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac8OMe). A library of 64 structurally distinct glycosphingolipid glycans belonging to ganglio-series, lacto-/neolacto-series, and globo-/isoglobo-series glycosphingolipid glycans is constructed. These glycans are essential standards and invaluable probes for bioassays and biomedical studies.
Figures






References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

