Impact of TIEG1 Deletion on the Passive Mechanical Properties of Fast and Slow Twitch Skeletal Muscles in Female Mice
- PMID: 27736981
- PMCID: PMC5063386
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164566
Impact of TIEG1 Deletion on the Passive Mechanical Properties of Fast and Slow Twitch Skeletal Muscles in Female Mice
Abstract
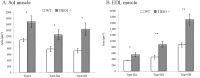
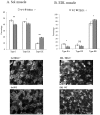
As transforming growth factor (TGF)-β inducible early gene-1 is highly expressed in skeletal muscle, the effect of TIEG1 gene deletion on the passive mechanical properties of slow and fast twitch muscle fibers was analyzed. Twenty five muscle fibers were harvested from soleus (Sol) and extensor digitorum longus (EDL) muscles from TIEG1-/- (N = 5) and control (N = 5) mice. Mechanical tests were performed on fibers and the dynamic and static stresses were measured. A viscoelastic Hill model of 3rd order was used to fit the experimental relaxation test data. In parallel, immunohistochemical analyses were performed on three serial transverse sections to detect the myosin isoforms within the slow and fast muscles. The percentage and the mean cross sectional area of each fiber type were calculated. These tests revealed a significant increase in the mechanical stress properties for the TIEG1-/- Sol fibers while a significant decrease appeared for the TIEG1-/- EDL fibers. Hill model tracked the shape of the experimental relaxation curve for both genotypes and both fiber types. Immunohistochemical results showed hypertrophy of all fiber types for TIEG1-/- muscles with an increase in the percentage of glycolytic fibers (IIX, and IIB) and a decrease of oxidative fibers (I, and IIA). This study has provided new insights into the role of TIEG1, known as KLF10, in the functional (SoltypeI: more resistant, EDLtypeIIB: less resistant) and morphological (glycolytic hypertrophy) properties of fast and slow twitch skeletal muscles. Further investigation at the cellular level will better reveal the role of the TIEG1 gene in skeletal muscle tissue.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





References
-
- Blok LJ, Grossmann ME, Perry JE, Tindall DJ. Characterization of an early growth-response gene, which encodes a zinc-finger transcription factor, potentially involved in cell-cycle regulation. Molecular Endocrinology. 1995;9(11):1610–20. 10.1210/mend.9.11.8584037. WOS:A1995TD09500018. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hefferan TE, Reinholz GG, Rickard DJ, Johnsen SA, Waters KM, Subramaniam M, et al. Overexpression of a nuclear protein, TIEG, mimics transforming growth factor-beta action in human osteoblast cells. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2000;275(27):20255–9. Epub 2000/05/19. 10.1074/jbc.C000135200 . - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

