INTRAMEDULLARY TUBERCULOMA OF THORACIC SPINAL CORD IN AN APPARENTLY HEALTHY NIGERIAN: CASE REPORT
- PMID: 27738623
- PMCID: PMC5020892
INTRAMEDULLARY TUBERCULOMA OF THORACIC SPINAL CORD IN AN APPARENTLY HEALTHY NIGERIAN: CASE REPORT
Abstract
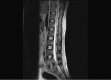
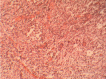
Spinal intramedullary is an uncommon form of tuberculosis causing spinal cord injury in this environment. We report a case of thoracic intramedullary tuberculoma in an immunocompetent male Nigerian with negative screening for tuberculosis. He presented with 8 months history of back pain and 2 months history of progressive weakness in both lower limbs. Physical examination revealed a well-nourished man with spastic paraplegia. Chest radiograph and CT scan were normal but Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the thoracolumbar region showed cord oedema and circumscribed intramedullary lesions at D12 and L1 levels with target sign. The patient was promptly prepared and had D12 and L1 laminectomy and posterior myelotomy with excision of the intramedullary lesion. Histology showed granulomatous lesion with central caseation in keeping with a tuberculoma. He was treated with a 4-drug antituberculous regimen with physiotherapy and he made complete neurological recovery 8 months post-operatively. Intramedullary tuberculoma should be considered in differential diagnosis of intramedullary tumors in this environment. Treatment with antituberculous drugs results in good outcome.
Keywords: Good outcome; Immunocompetent patient; Intramedullary spinal tuberculoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Liu YD, Wang FY, Xu JM, Guan Y, Guan H. Intramedullary thoracic tuberculoma. Spinal cord. 2010;48:80–82. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources