7-Ketocholesterol induces ATM/ATR, Chk1/Chk2, PI3K/Akt signalings, cytotoxicity and IL-8 production in endothelial cells
- PMID: 27740938
- PMCID: PMC5342680
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.12578
7-Ketocholesterol induces ATM/ATR, Chk1/Chk2, PI3K/Akt signalings, cytotoxicity and IL-8 production in endothelial cells
Abstract
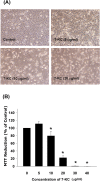
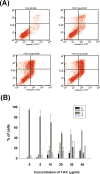
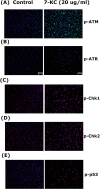
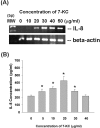
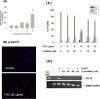
Cardiovascular diseases (atherosclerosis, stroke, myocardiac infarction etc.) are the major systemic diseases of elder peoples in the world. This is possibly due to increased levels of oxidized low-density lipoproteins (oxLDLs) such as 7-ketocholesterol (7-KC) and lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) that damage vascular endothelial cells, induce inflammatory responses, to elevate the risk of cardiovascular diseases, Alzheimer's disease, and age-related macular degeneration. However the toxic effects of 7-KC on endothelial cells are not known. In this study, 7-KC showed cytotoxicity to endothelial cells at concentrations higher than 10 µg/ml. 7-KC stimulated ATM/Chk2, ATR-Chk1 and p53 signaling pathways in endothelial cells. 7-KC also induced G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis with an inhibition of Cyclin dependent kinase 1 (Cdk1) and cyclin B1 expression. Secretion and expression of IL-8 in endothelial cells were stimulated by 7-KC. 7-KC further induced intracellular ROS production as shown by increase in DCF fluorescence and Akt phosphorylation. LY294002 attenuated the 7-KC-induced apoptosis and IL-8 mRNA expression of endothelial cells. These results indicate that oxLDLs such as 7-KC may contribute to the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis, thrombosis and cardiovascular diseases by induction of endothelial damage, apoptosis and inflammatory responses. These events are associated with ROS production, activation of ATM/Chk2, ATR/Chk1, p53 and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways.
Keywords: Gerotarget; apoptosis; atherosclerosis; cytotoxicity; endothelial cells; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest for this submission.
Figures


References
-
- Bourdon E, Loreau N, Davignon J, Bernier L, Blache D. Involvement of oxysterols and lysophosphatidylcholine in the oxidized LDL-induced impairment of serum albumin synthesis by HEPG2 cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000;20:2643–2650. - PubMed
-
- Hughes H, Mathews B, Lenz ML, Guyton JR. Cytotoxicity of oxidized LDL to porcine aortic smooth muscle cells is associated with the oxysterols 7-ketocholesterol and 7-hydroxycholesterol. Arterioscler Thromb. 1994;14:1177–1185. - PubMed
-
- Lyon MA, Brown AJ. 7-Ketocholesterol. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1999;31:369–375. - PubMed
-
- Gramajo AL, Zacharias LC, Neekhra A, Luthra S, Atilano SR, Chwa M, Brown DJ, Kuppermann BD, Kenney MC. Mitochondrial DNA damage induced by 7-ketocholesterol in human retina pigment epithelial cells in vitro. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010;51:1164–1170. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

