Factors Influencing Engagement, Perceived Usefulness and Behavioral Mechanisms Associated with a Text Message Support Program
- PMID: 27741244
- PMCID: PMC5065147
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163929
Factors Influencing Engagement, Perceived Usefulness and Behavioral Mechanisms Associated with a Text Message Support Program
Abstract
Introduction: Many studies have now demonstrated the efficacy of text messaging in positively changing behaviours. We aimed to identify features and factors that explain the effectiveness of a successful text messaging program in terms of user engagement, perceived usefulness, behavior change and program delivery preferences.
Methods: Mixed methods qualitative design combining four data sources; (i) analytic data extracted directly from the software system, (ii) participant survey, (iii) focus groups to identify barriers and enablers to implementation and mechanisms of effect and (iv) recruitment screening logs and text message responses to examine engagement. This evaluation was conducted within the TEXT ME trial-a parallel design, single-blind randomized controlled trial (RCT) of 710 patients with coronary heart disease (CHD). Qualitative data were interpreted using inductive thematic analysis.
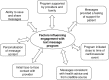
Results: 307/352 (87% response rate) of recruited patients with CHD completed the program evaluation survey at six months and 25 participated in a focus group. Factors increasing engagement included (i) ability to save and share messages, (ii) having the support of providers and family, (iii) a feeling of support through participation in the program, (iv) the program being initiated close to the time of a cardiovascular event, (v) personalization of the messages, (vi) opportunity for initial face-to-face contact with a provider and (vii) that program and content was perceived to be from a credible source. Clear themes relating to program delivery were that diet and physical activity messages were most valued, four messages per week was ideal and most participants felt program duration should be provided for at least for six months or longer.
Conclusions: This study provides context and insight into the factors influencing consumer engagement with a text message program aimed at improving health-related behavior. The study suggests program components that may enhance potential success but will require integration at the development stage to optimize up-scaling.
Trial registration: Australia and New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry, ACTRN12611000161921.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organisation: The top 10 cause of death. Fact Sheet No 310. Updated May 2014. ed. 2014.
-
- Hardoon SL, Whincup PH, Lennon LT, Wannamethee SG, Capewell S, Morris RW. How much of the recent decline in the incidence of myocardial infarction in British men can be explained by changes in cardiovascular risk factors? Evidence from a prospective population-based study. Circulation. 2008;117:598–604. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.705947 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources