Chronic hepatitis C virus infection and pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 27741441
- PMCID: PMC5120759
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coviro.2016.09.010
Chronic hepatitis C virus infection and pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
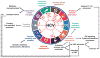
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is one of the major causes of advanced liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) worldwide. While the knowledge about the molecular virology of HCV infection has markedly advanced, the molecular mechanisms of disease progression leading to fibrosis, cirrhosis and HCC are still unclear. Accumulating experimental and clinical studies indicate that HCV may drive hepatocarcinogenesis directly via its proteins or transcripts, and/or indirectly through induction of chronic liver inflammation. Despite the possibility to eradicate HCV infection through direct-acting antiviral treatment, the risk of HCC persists although specific biomarkers to estimate this risk are still missing. Thus, a better understanding of HCV-induced HCC and more physiological liver disease models are required to prevent cancer development.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interest The authors do not have any conflict of interest and did not receive writing assistance.
Figures
References
-
- El-Serag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:1118–1127. - PubMed
-
- Hajarizadeh B, Grebely J, Dore GJ. Epidemiology and natural history of HCV infection. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;10:553–562. - PubMed
-
- Chung RT, Baumert TF. Curing chronic hepatitis C--the arc of a medical triumph. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:1576–1578. - PubMed
-
- Morgan RL, Baack B, Smith BD, Yartel A, Pitasi M, Falck-Ytter Y. Eradication of hepatitis C virus infection and the development of hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Ann Intern Med. 2013;158:329–337. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

