Disease-causing point-mutations in metal-binding domains of Wilson disease protein decrease stability and increase structural dynamics
- PMID: 27744583
- PMCID: PMC5285417
- DOI: 10.1007/s10534-016-9976-7
Disease-causing point-mutations in metal-binding domains of Wilson disease protein decrease stability and increase structural dynamics
Abstract
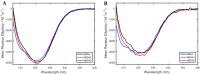
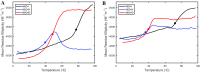
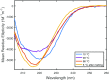
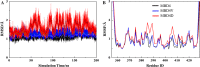
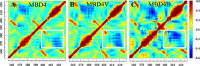
After cellular uptake, Copper (Cu) ions are transferred from the chaperone Atox1 to the Wilson disease protein (ATP7B) for incorporation into Cu-dependent enzymes in the secretory pathway. Human ATP7B is a large multi-domain membrane-spanning protein which, in contrast to homologues in other organisms, has six similar cytoplasmic metal-binding domains (MBDs). The reason for multiple MBDs is proposed to be indirect modulation of enzymatic activity and it is thus intriguing that point mutations in MBDs can promote Wilson disease. We here investigated, in vitro and in silico, the biophysical consequences of clinically-observed Wilson disease mutations, G85V in MBD1 and G591D in MBD6, incorporated in domain 4. Because G85 and G591 correspond to a conserved Gly found in all MBDs, we introduced the mutations in the well-characterized MBD4. We found the mutations to dramatically reduce the MBD4 thermal stability, shifting the midpoint temperature of unfolding by more than 20 °C. In contrast to wild type MBD4 and MBD4D, MBD4V adopted a misfolded structure with a large β-sheet content at high temperatures. Molecular dynamic simulations demonstrated that the mutations increased backbone fluctuations that extended throughout the domain. Our findings imply that reduced stability and enhanced dynamics of MBD1 or MBD6 is the origin of ATP7B dysfunction in Wilson disease patients with the G85V or G591D mutation.
Keywords: ATP7B; Circular dichroism; Metal-binding domain; Molecular dynamics; Thermal stability; Wilson disease.
Figures

References
-
- Achila D, Banci L, Bertini I, Bunce J, Ciofi-Baffoni S, Huffman DL. Structure of human Wilson protein domains 5 and 6 and their interplay with domain 4 and the copper chaperone HAH1 in copper uptake. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(15):5729–5734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0504472103. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

