ALKBH1-Mediated tRNA Demethylation Regulates Translation
- PMID: 27745969
- PMCID: PMC5119773
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.09.038
ALKBH1-Mediated tRNA Demethylation Regulates Translation
Abstract
tRNA is a central component of protein synthesis and the cell signaling network. One salient feature of tRNA is its heavily modified status, which can critically impact its function. Here, we show that mammalian ALKBH1 is a tRNA demethylase. It mediates the demethylation of N1-methyladenosine (m1A) in tRNAs. The ALKBH1-catalyzed demethylation of the target tRNAs results in attenuated translation initiation and decreased usage of tRNAs in protein synthesis. This process is dynamic and responds to glucose availability to affect translation. Our results uncover reversible methylation of tRNA as a new mechanism of post-transcriptional gene expression regulation.
Keywords: ALKBH1; N(1)-methyladenosine (m(1)A); codon usage; dynamic tRNA modification; tRNA demethylase; tRNA demethylation; tRNA methylation; translation elongation; translation initiation; translation regulation.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


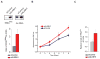
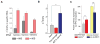
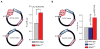

References
-
- Aas PA, Otterlei M, Falnes PO, Vagbo CB, Skorpen F, Akbari M, Sundheim O, Bjoras M, Slupphaug G, Seeberg E, et al. Human and bacterial oxidative demethylases repair alkylation damage in both RNA and DNA. Nature. 2003;421:859–863. - PubMed
-
- Agris PF, Vendeix FAP, Graham WD. tRNA’s Wobble Decoding of the Genome: 40 Years of Modification. J Mol Biol. 2007;366:1–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

