An LXR-Cholesterol Axis Creates a Metabolic Co-Dependency for Brain Cancers
- PMID: 27746144
- PMCID: PMC5479636
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.09.008
An LXR-Cholesterol Axis Creates a Metabolic Co-Dependency for Brain Cancers
Abstract
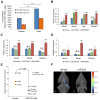
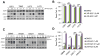
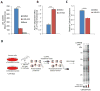
Small-molecule inhibitors targeting growth factor receptors have failed to show efficacy for brain cancers, potentially due to their inability to achieve sufficient drug levels in the CNS. Targeting non-oncogene tumor co-dependencies provides an alternative approach, particularly if drugs with high brain penetration can be identified. Here we demonstrate that the highly lethal brain cancer glioblastoma (GBM) is remarkably dependent on cholesterol for survival, rendering these tumors sensitive to Liver X receptor (LXR) agonist-dependent cell death. We show that LXR-623, a clinically viable, highly brain-penetrant LXRα-partial/LXRβ-full agonist selectively kills GBM cells in an LXRβ- and cholesterol-dependent fashion, causing tumor regression and prolonged survival in mouse models. Thus, a metabolic co-dependency provides a pharmacological means to kill growth factor-activated cancers in the CNS.
Keywords: brain cancer; cholesterol; glioblastoma; liver X receptor; metabolism; oxysterols.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




Comment on
-
Cholesterol: An Achilles' Heel for Glioblastoma?Cancer Cell. 2016 Nov 14;30(5):653-654. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.10.011. Cancer Cell. 2016. PMID: 27846382
References
-
- Björkhem I. Crossing the barrier: oxysterols as cholesterol transporters and metabolic modulators in the brain. J Intern Med. 2006;260:493–508. - PubMed
-
- Björkhem I, Meaney S. Brain cholesterol: long secret life behind a barrier. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004;24:806–815. - PubMed
-
- Bovenga F, Sabbà C, Moschetta A. Uncoupling nuclear receptor LXR and cholesterol metabolism in cancer. Cell Metab. 2015;21:517–526. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

