Microbial contamination of removable dental prosthesis at different interval of usage: An in vitro study
- PMID: 27746598
- PMCID: PMC5062147
- DOI: 10.4103/0972-4052.176536
Microbial contamination of removable dental prosthesis at different interval of usage: An in vitro study
Abstract
Background: Loss of teeth affects the individual's health. Many factors determine the need to wear a removable dental prosthesis. Due to nature of design, age and lack of awareness, prosthesis often are neglected to maintain in an aseptic condition leading to microbial contamination. This provided an impetus for the present study with the aim of determining the microbial contamination of removable dental prosthesis.
Methodology: Total, 45 patients wearing removable dental prosthesis were randomly selected. Patients were divided into three groups as per duration of usage since 1 month, 6 month and ≥1 year. Sterile cotton swab moistened with phosphate buffer saline (PBS) was used to collect swab from the fitting areas of prosthesis. Swab samples was inserted immediately into the sterile tube containing 1 ml of PBS solution, 10 μl PBS is inoculated on the blood agar and MacConkey agar plates using spread plate technique. Samples were cultured and incubated at 37°C for 48 h. Calibrated microbiologist isolated, identified and counted microorganisms using colony counter. Depending on the nature of data, statistical analysis was done applying Kruskal-Wallis test, Mann-Whitney U-test and Chi-square test.
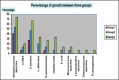
Result: Streptococcus species and Staphylococcus aureus were the common microorganisms isolated in all three groups and was statistically significant at P <0.05. Candida albicans, Diptheroid, Escherichia coli, Micrococcus species were isolated from Group II and Group III.
Conclusion: There is a linear increase in microbial contamination of removable dental prosthesis as the duration of usage increases and might increase the susceptibility of individuals' to many diseases.
Keywords: Denture; microbial contamination; removable dental prosthesis.
Figures
References
-
- Shah N, Parkash H, Sunderam KR. Edentulousness, denture wear and denture needs of Indian elderly – A community-based study. J Oral Rehabil. 2004;31:467–76. - PubMed
-
- Ngatia EM, Gathece LW, Macigo FG, Mulli TK, Mutara LN, Wagaiyu EG. Nutritional and oral health status of an elderly population in Nairobi. East Afr Med J. 2008;85:378–85. - PubMed
-
- Kar S, Tripathi A. Prevalence of type of removable dentures in elderly citizens in Northern India. J Contemp Dent. 2015;5:76–9.
-
- Krawczyk J, Bożyk A, Kiworkowa-Rączkowska E, Berger M, Bakalczuk M, Szkutnik J, et al. Hygiene, ways of storage and lifetime of removable dentures. J Pre-Clin Clin Res. 2015;9:54–6.
-
- Ghamrawy EE. Quantitative changes in dental plaque formation related to removable partial dentures. J Oral Rehabil. 1976;3:115–20. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources