Silibinin Inhibits Proliferation and Migration of Human Hepatic Stellate LX-2 Cells
- PMID: 27746612
- PMCID: PMC5052367
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jceh.2016.01.002
Silibinin Inhibits Proliferation and Migration of Human Hepatic Stellate LX-2 Cells
Abstract
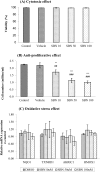
Background: Proliferation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) play pivotal role in the progression of hepatic fibrosis consequent to chronic liver injury. Silibinin (SBN), a flavonoid compound, has shown to possess cell cycle arresting potential against many actively proliferating cancers cell lines. The objective of this study was to evaluate the anti-proliferative and cell cycle arresting properties of SBN in rapidly proliferating human hepatic stellate LX-2 cell line.
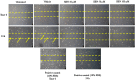
Methods: LX-2 cells were fed with culture medium supplemented with different concentrations of SBN (10, 50 and 100 μM). After 24 and 96 h of treatment, total cell number was determined by counting. Cytotoxicity was evaluated by trypan blue dye exclusion test. The expression profile of cMyc and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPAR-γ) protein expressions was evaluated by Western blotting. Oxidative stress marker genes profile was quantified using qPCR. The migratory response of HSCs was observed by scrape wound healing assay.
Results: SBN treatments significantly inhibit the LX-2 cell proliferation (without affecting its viability) in dose dependent manner. This treatment also retards the migration of LX-2 cells toward injured area. In Western blotting studies SBN treatment up regulated the protein expressions of PPAR-γ and inhibited cMyc.
Conclusion: The present study shows that SBN retards the proliferation, activation and migration of LX-2 cells without inducing cytotoxicity and oxidative stress. The profound effects could be due to cell cycle arresting potential of SBN.
Keywords: AKR1C1, aldo-keto reductase family 1, member C1; ARE, antioxidant responsive element; CDKI, cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor; CYP450, cytochrome P450; DMEM, Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium; DMSO, dimethylsulphoxide; ECM, extracellular matrix; FBS, fetal bovine serum; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; HMOX1, heme oxygenase (decycling) 1; HSCs, hepatic stellate cells; NQO1, NAD(P)H dehydrogenase, quinone 1; Nrf-2, nuclear respiratory factor; PPAR-γ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ; PPIA, peptidylprolyl isomerase A; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SBN, silibinin; TXNRD1, thioredoxin reductase 1; cytotoxicity; hepatic stellate cells; oxidative stress; qPCR, quantitative polymerase chain reaction; wound healing.
Figures


References
-
- Guimarães E.L., Stradiot L., Mannaerts I. P311 modulates hepatic stellate cells migration. Liver Int. 2015;35(4):1253–1264. - PubMed
-
- Bitencourt S., Mesquita F., Basso B. Capsaicin modulates proliferation, migration, and activation of hepatic stellate cells. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014;68(2):387–396. - PubMed
-
- Raghu R., Jesudas B., Bhavani G. Silibinin mitigates zidovudine-induced hepatocellular degenerative changes, oxidative stress and hyperlipidaemia in rats. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2015;34(January (11)):1031–1042. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

