Single centre experience on short bar technique for pectus excavatum
- PMID: 27747178
- PMCID: PMC5056931
- DOI: 10.21037/acs.2016.09.05
Single centre experience on short bar technique for pectus excavatum
Abstract
Background: Pectus excavatum (PE) is the most frequent anomaly of the anterior chest wall. Before 2001, all patients in Denmark were referred to the plastic and reconstructive surgeon for implantation of a subcutaneous silicone prosthesis, because the modified Ravitch procedure was not used. Since 2001, all patients have been treated with a modified Nuss procedure, which today has become the gold standard for correction of PE.
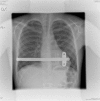
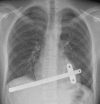
Methods: From September 2001 to March 2016, 1,713 patients have been operated by a modified Nuss procedure using the short bar at Aarhus University Hospital with a male-female ratio 6:1. The median age was 16 years (range 7-58 years). All operations were done in general anesthesia with epidural analgesia and all patients were operated by the same surgeon. All patients were seen routinely 6 weeks after surgery and the bars were removed after 3 years.
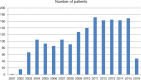
Results: Patients were younger than 18 years in 1,109 cases (65%). The number of bars needed for optimal correction was one in 1,209 patients, two in 486 patients and three in 18 patients. The median length of bar changed from 11 inches to 10 inches during the study period. The annual number of procedures continued to rise during the study period [833 patients during the first 10 years and 880 patients in the last 6 years, though more patients received two bars in the later period, (34%) versus (24%)] and the proportion of patients older than 30 years increased from 7.7% to 10%. The average duration of the operation was 36 minutes (range 12-270 minutes) and did not change significantly during the study period, change in operation time which was around half an hour. The median postoperative hospital stay decreased over time from 6 to 2 days. There was no mortality.
Conclusions: The modified Nuss procedure with the short bar technique is effective for the correction of PE. The results are stable with a low rate of bar malrotations, and in may most cases can be done in less than an hour in experienced hands.
Keywords: Nuss; Pectus excavatum repair; minimally invasive; short bar; surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Pilegaard is a consultant at Zimmer Biomet.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Nuss technique in pectus excavatum: a mono-institutional experience.J Thorac Dis. 2015 Apr;7(Suppl 2):S172-6. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2015.04.07. J Thorac Dis. 2015. PMID: 25984364 Free PMC article.
-
Early experience with the Nuss minimally invasive correction of pectus excavatum in adults.World J Surg. 2002 Oct;26(10):1217-21. doi: 10.1007/s00268-002-6519-x. Epub 2002 Sep 6. World J Surg. 2002. PMID: 12209230
-
Correction of pectus excavatum using the modified Nuss procedure, ad modum Pilegaard.Multimed Man Cardiothorac Surg. 2018 Jun 12;2018. doi: 10.1510/mmcts.2018.028. Multimed Man Cardiothorac Surg. 2018. PMID: 30070782
-
Short Nuss bar procedure.Ann Cardiothorac Surg. 2016 Sep;5(5):513-518. doi: 10.21037/acs.2016.09.06. Ann Cardiothorac Surg. 2016. PMID: 27747185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anesthesia for minimally invasive chest wall reconstructive surgeries: Our experience and review of literature.Saudi J Anaesth. 2017 Jul-Sep;11(3):319-326. doi: 10.4103/sja.SJA_13_17. Saudi J Anaesth. 2017. PMID: 28757834 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Musculoskeletal diseases in Marfan syndrome: a nationwide registry study.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2022 Mar 5;17(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s13023-022-02272-2. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2022. PMID: 35248143 Free PMC article.
-
The management of pectus excavatum in pediatric patients: a narrative review.Transl Pediatr. 2023 Feb 28;12(2):208-220. doi: 10.21037/tp-22-361. Epub 2023 Jan 31. Transl Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 36891368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Outcomes in adult pectus excavatum patients undergoing Nuss repair.Patient Relat Outcome Meas. 2018 Jan 30;9:65-90. doi: 10.2147/PROM.S117771. eCollection 2018. Patient Relat Outcome Meas. 2018. PMID: 29430201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The questionable benefit of pectus excavatum repair on cardiopulmonary function: a prospective study.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2021 Dec 27;61(1):75-82. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezab296. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2021. PMID: 34263302 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Incidence and severity of surgical complications after pectus excavatum bar removal.Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2021 Jul 26;33(2):237-241. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivab077. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2021. PMID: 34310684 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
