The Multifaceted Activity of the VirF Regulatory Protein in the Shigella Lifestyle
- PMID: 27747215
- PMCID: PMC5041530
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2016.00061
The Multifaceted Activity of the VirF Regulatory Protein in the Shigella Lifestyle
Abstract
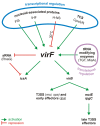
Shigella is a highly adapted human pathogen, mainly found in the developing world and causing a severe enteric syndrome. The highly sophisticated infectious strategy of Shigella banks on the capacity to invade the intestinal epithelial barrier and cause its inflammatory destruction. The cellular pathogenesis and clinical presentation of shigellosis are the sum of the complex action of a large number of bacterial virulence factors mainly located on a large virulence plasmid (pINV). The expression of pINV genes is controlled by multiple environmental stimuli through a regulatory cascade involving proteins and sRNAs encoded by both the pINV and the chromosome. The primary regulator of the virulence phenotype is VirF, a DNA-binding protein belonging to the AraC family of transcriptional regulators. The virF gene, located on the pINV, is expressed only within the host, mainly in response to the temperature transition occurring when the bacterium transits from the outer environment to the intestinal milieu. VirF then acts as anti-H-NS protein and directly activates the icsA and virB genes, triggering the full expression of the invasion program of Shigella. In this review we will focus on the structure of VirF, on its sophisticated regulation, and on its role as major player in the path leading from the non-invasive to the invasive phenotype of Shigella. We will address also the involvement of VirF in mechanisms aimed at withstanding adverse conditions inside the host, indicating that this protein is emerging as a global regulator whose action is not limited to virulence systems. Finally, we will discuss recent observations conferring VirF the potential of a novel antibacterial target for shigellosis.
Keywords: AraC proteins; DNA binding proteins; Shigella; VirF; antivirulence therapy; bacterial virulence; pathogenic E. coli; transcriptional regulators.
Figures

Similar articles
-
H-NS regulation of virulence gene expression in enteroinvasive Escherichia coli harboring the virulence plasmid integrated into the host chromosome.J Bacteriol. 1995 Aug;177(16):4703-12. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.16.4703-4712.1995. J Bacteriol. 1995. PMID: 7642498 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the virulence plasmid-carried apyrase gene (apy) of enteroinvasive Escherichia coli and Shigella flexneri is under the control of H-NS and the VirF and VirB regulatory cascade.Infect Immun. 1998 Oct;66(10):4957-64. doi: 10.1128/IAI.66.10.4957-4964.1998. Infect Immun. 1998. PMID: 9746603 Free PMC article.
-
The AraC/XylS Protein MxiE and Its Coregulator IpgC Control a Negative Feedback Loop in the Transcriptional Cascade That Regulates Type III Secretion in Shigella flexneri.J Bacteriol. 2022 Jul 19;204(7):e0013722. doi: 10.1128/jb.00137-22. Epub 2022 Jun 15. J Bacteriol. 2022. PMID: 35703565 Free PMC article.
-
A Tale about Shigella: Evolution, Plasmid, and Virulence.Microorganisms. 2023 Jun 30;11(7):1709. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11071709. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37512882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Intriguing Evolutionary Journey of Enteroinvasive E. coli (EIEC) toward Pathogenicity.Front Microbiol. 2017 Dec 5;8:2390. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02390. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29259590 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The genomic epidemiology of shigellosis in South Africa.Nat Commun. 2023 Nov 24;14(1):7715. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-43345-5. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 38001075 Free PMC article.
-
Remodulation of bacterial transcriptome after acquisition of foreign DNA: the case of irp-HPI high-pathogenicity island in Vibrio anguillarum.mSphere. 2024 Jan 30;9(1):e0059623. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00596-23. Epub 2023 Dec 11. mSphere. 2024. PMID: 38078732 Free PMC article.
-
The VirF21:VirF30 protein ratio is affected by temperature and impacts Shigella flexneri host cell invasion.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2022 Jun 22;369(1):fnac043. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnac043. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2022. PMID: 35521699 Free PMC article.
-
Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron Outer Membrane Vesicles Modulate Virulence of Shigella flexneri.mBio. 2022 Oct 26;13(5):e0236022. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02360-22. Epub 2022 Sep 14. mBio. 2022. PMID: 36102517 Free PMC article.
-
The NEL Family of Bacterial E3 Ubiquitin Ligases.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 13;23(14):7725. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147725. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35887072 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

