A piezo surgery with corticotomies and implant placement as part of a multidisciplinary approach to treat malocclusion disorder in an adult patient: clinical report
- PMID: 27747645
- PMCID: PMC5005651
- DOI: 10.1186/s40729-015-0021-3
A piezo surgery with corticotomies and implant placement as part of a multidisciplinary approach to treat malocclusion disorder in an adult patient: clinical report
Abstract
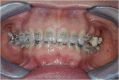
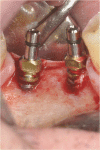
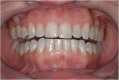
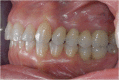
This clinical report illustrates a multidisciplinary approach for the rehabilitation of a young adult patient affected by a bilateral edentulous space and an anterior deep bite. The patient required orthodontics and surgical corticotomy and implantology (both performed with a piezo device). A multidisciplinary planning approach, including orthodontics, oral and periodontic surgery, and restorative dentistry, has an important role in the final outcome of treatment. In fact a dental class I occlusion has been established only on the right side. The left side could not be restored to an ideal class I relationship due to the pontic prosthesis. The original collapsed right posterior occlusion was corrected. A stable posterior occlusion was established, and the balancing interference was eliminated. Centric relation and centric occlusion were established at the same vertical dimension of occlusion. The cephalometric analysis and clinical aspect at the end of treatment showed that the patient had improvements in overbite and overjet.Multidisciplinary management, including endodontic and restorative dentistry, periodontics, corticotomy-assisted orthodontics, implants, and prosthetics, was used for a young female patient with multiple missing teeth, anterior deep bite, and a malocclusion with cant of the occlusal plane. The interaction of interdisciplinary specialties and careful treatment planning were required. The patient also benefited esthetically from our effort.
Keywords: Corticotomies; Multidisciplinary approach; Oral implantology; Piezo device.
Figures

















References
-
- Bonetti GA, Giunta D. Molar intrusion with a removable appliance. J Clin Orthod. 1996;30:434–437. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

