Irregular vascular pattern by contrast-enhanced ultrasonography and high serum Lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive fraction of alpha-fetoprotein level predict poor outcome after successful radiofrequency ablation in patients with early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 27748052
- PMCID: PMC5119966
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.932
Irregular vascular pattern by contrast-enhanced ultrasonography and high serum Lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive fraction of alpha-fetoprotein level predict poor outcome after successful radiofrequency ablation in patients with early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
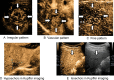
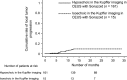
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is considered the most effective treatment for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients unsuitable for resection. However, poor outcome after RFA has occasionally been reported worldwide. To predict such an outcome, we investigated imaging findings using contrast-enhanced ultrasonography (CEUS) with Sonazoid and serum tumor markers before RFA. This study included 176 early-stage HCC patients who had initially achieved successful RFA. Patients were examined using CEUS; their levels of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), Lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive fraction of AFP (AFP-L3), and des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin before RFA were measured. Sonazoid provided parenchyma-specific contrast imaging and facilitated tumor vascular architecture imaging through maximum intensity projection (MIP). Kaplan-Meier analysis examined cumulative rates of local tumor progression, intrasubsegmental recurrence, and survival; factors associated with these were determined with Cox proportional hazards analysis. Local tumor progression (n = 15), intrasubsegmental recurrence (n = 46), and death (n = 18) were observed. Irregular pattern in MIP classification and serum AFP-L3 level (>10%) before RFA were identified as independent risk factors for local tumor progression and intrasubsegmental recurrence. These two factors were independently associated with poor survival after RFA (irregular pattern in MIP: hazard ratio, (HR) = 8.26; 95% confidence interval, (CI) = 2.24-30.3; P = 0.002 and AFP-L3 > 10%: HR = 2.94; 95% CI = 1.09-7.94; P = 0.033). Irregular MIP pattern by CEUS and high level of serum AFP-L3 were independent risk factors for poor outcome after successful RFA. The Patients with these findings should be considered as special high-risk group in early-stage HCC.
Keywords: Alpha-fetoprotein; contrast-enhanced ultrasonography; hepatocellular carcinoma; intrasubsegmental recurrence; poor survival; radiofrequency ablation.
© 2016 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Torre, L. A. , Bray F., Siegel R. L., Ferlay J., Lortet‐Tieulent J., and Jemal A.. 2012. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015. 65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Tateishi, R. , Shiina S., Teratani T., Obi S., Sato S., Koike Y., et al. 2005. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. An analysis of 1000 cases. Cancer 103:1201–1209. - PubMed
-
- Lee, D. H. , Lee J. M., Lee J. Y., Kim S. H., Yoon J. H., Kim Y. J., et al. 2014. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma as first‐line treatment: long‐term results and prognostic factors in 162 patients with cirrhosis. Radiology 270:900–909. - PubMed
-
- Shin, S. , Lee J. M., Kim K. W., Joo I., Han J. K., B. I. Choi , et al. 2014. Postablation assessment using follow‐up registration of CT images before and after radiofrequency ablation (RFA): prospective evaluation of midterm therapeutic results of RFA for hepatocellular carcinoma. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 203:70–77. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

