Human genome-wide RNAi screen reveals host factors required for enterovirus 71 replication
- PMID: 27748395
- PMCID: PMC5071646
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms13150
Human genome-wide RNAi screen reveals host factors required for enterovirus 71 replication
Abstract
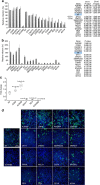
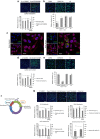
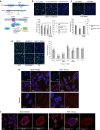
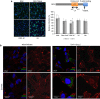
Enterovirus 71 (EV71) is a neurotropic enterovirus without antivirals or vaccine, and its host-pathogen interactions remain poorly understood. Here we use a human genome-wide RNAi screen to identify 256 host factors involved in EV71 replication in human rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Enrichment analyses reveal overrepresentation in processes like mitotic cell cycle and transcriptional regulation. We have carried out orthogonal experiments to characterize the roles of selected factors involved in cell cycle regulation and endoplasmatic reticulum-associated degradation. We demonstrate nuclear egress of CDK6 in EV71 infected cells, and identify CDK6 and AURKB as resistance factors. NGLY1, which co-localizes with EV71 replication complexes at the endoplasmatic reticulum, supports EV71 replication. We confirm importance of these factors for EV71 replication in a human neuronal cell line and for coxsackievirus A16 infection. A small molecule inhibitor of NGLY1 reduces EV71 replication. This study provides a comprehensive map of EV71 host factors and reveals potential antiviral targets.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[MiR373 and miR542-5p regulate the replication of enterovirus 71 in rhabdomyosarcoma cells].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2014 Jun;30(6):943-53. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2014. PMID: 25212011 Chinese.
-
Antiviral screen identifies EV71 inhibitors and reveals camptothecin-target, DNA topoisomerase 1 as a novel EV71 host factor.Antiviral Res. 2017 Jul;143:122-133. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2017.04.008. Epub 2017 Apr 17. Antiviral Res. 2017. PMID: 28427827
-
Validation-based insertional mutagenesis for identification of Nup214 as a host factor for EV71 replication in RD cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Aug 2;437(3):452-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.06.101. Epub 2013 Jul 3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013. PMID: 23831628
-
Host factors in enterovirus 71 replication.J Virol. 2011 Oct;85(19):9658-66. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05063-11. Epub 2011 Jun 29. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21715481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Molecular Mechanism of Action of hnRNP K and RTN3 in the Replication of Enterovirus 71].Bing Du Xue Bao. 2015 Mar;31(2):197-200. Bing Du Xue Bao. 2015. PMID: 26164948 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Influenza A virus co-opts ERI1 exonuclease bound to histone mRNA to promote viral transcription.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Oct 9;48(18):10428-10440. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa771. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32960265 Free PMC article.
-
The Structure, Function, and Mechanisms of Action of Enterovirus Non-structural Protein 2C.Front Microbiol. 2020 Dec 14;11:615965. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.615965. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33381104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pim1 Impacts Enterovirus A71 Replication and Represents a Potential Target in Antiviral Therapy.iScience. 2019 Sep 27;19:715-727. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2019.08.008. Epub 2019 Aug 8. iScience. 2019. PMID: 31476618 Free PMC article.
-
SLC35B2 Acts in a Dual Role in the Host Sulfation Required for EV71 Infection.J Virol. 2022 May 11;96(9):e0204221. doi: 10.1128/jvi.02042-21. Epub 2022 Apr 14. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35420441 Free PMC article.
-
2018 international meeting of the Global Virus Network.Antiviral Res. 2019 Mar;163:140-148. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2019.01.013. Epub 2019 Jan 25. Antiviral Res. 2019. PMID: 30690044 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schmidt N. J., Lennette E. H. & Ho H. H. An apparently new enterovirus isolated from patients with disease of the central nervous system. J. Infect. Dis. 129, 304–309 (1974). - PubMed
-
- Ho M. et al.. An epidemic of enterovirus 71 infection in Taiwan. Taiwan Enterovirus Epidemic Working Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 341, 929–935 (1999). - PubMed
-
- McMinn P. C. An overview of the evolution of enterovirus 71 and its clinical and public health significance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 26, 91–107 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Ahmad K. Hand, foot, and mouth disease outbreak reported in Singapore. The Lancet 356, 1338 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Chang L.-Y. et al.. Neurodevelopment and cognition in children after enterovirus 71 infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 356, 1226–1234 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

