Protective effects of Centella asiatica leaf extract on dimethylnitrosamine‑induced liver injury in rats
- PMID: 27748812
- PMCID: PMC5101987
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5809
Protective effects of Centella asiatica leaf extract on dimethylnitrosamine‑induced liver injury in rats
Abstract
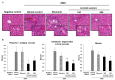
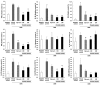
Oxidative stress in liver injury is a major pathogenetic factor in the progression of liver damage. Centella asiatica (L.) Urban, known in the United States as Gotu kola, is widely used as a traditional herbal medicine in Chinese or Indian Pennywort. The efficacy of Centella asiatica is comprehensive and is used as an anti‑inflammatory agent, for memory improvement, for its antitumor activity and for treatment of gastric ulcers. The present study investigated the protective effects of Centella asiatica on dimethylnitrosamine (DMN)‑induced liver injury in rats. The rats in the treatment groups were treated with Centella asiatica at either 100 or 200 mg/kg in distilled water (D.W) or with silymarin (200 mg/kg in D.W) by oral administration for 5 days daily following intraperitoneal injections of 30 mg/kg DMN. Centella asiatica significantly decreased the relative liver weights in the DMN‑induced liver injury group, compared with the control. The assessment of liver histology showed that Centella asiatica significantly alleviated mass periportal ± bridging necrosis, intralobular degeneration and focal necrosis, with fibrosis of liver tissues. Additionally, Centella asiatica significantly decreased the level of malondialdehyde, significantly increased the levels of antioxidant enzymes, including superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase and catalase, and may have provided protection against the deleterious effects of reactive oxygen species. In addition, Centella asiatica significantly decreased inflammatory mediators, including interleukin (IL)‑1β, IL‑2, IL‑6, IL‑10, IL‑12, tumor necrosis factor‑α, interferon‑γ and granulocyte/macrophage colony‑stimulating factor. These results suggested that Centella asiatica had hepatoprotective effects through increasing the levels of antioxidant enzymes and reducing the levels of inflammatory mediators in rats with DMN‑induced liver injury. Therefore, Centella asiatica may be useful in preventing liver damage.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of Centella asiatica on arsenic induced oxidative stress and metal distribution in rats.J Appl Toxicol. 2006 May-Jun;26(3):213-22. doi: 10.1002/jat.1131. J Appl Toxicol. 2006. PMID: 16389662
-
Beneficial effects of Centella asiatica aqueous extract against arsenic-induced oxidative stress and essential metal status in rats.Phytother Res. 2007 Oct;21(10):980-8. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2208. Phytother Res. 2007. PMID: 17600859
-
Oral administration of Centella asiatica (L.) Urb leave aqueous extract ameliorates cerebral oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis in male rats with type-2 diabetes.Inflammopharmacology. 2020 Dec;28(6):1599-1622. doi: 10.1007/s10787-020-00733-3. Epub 2020 Jun 25. Inflammopharmacology. 2020. PMID: 32588370
-
Gotu Kola (Centella asiatica): Nutritional Properties and Plausible Health Benefits.Adv Food Nutr Res. 2015;76:125-57. doi: 10.1016/bs.afnr.2015.08.001. Epub 2015 Oct 1. Adv Food Nutr Res. 2015. PMID: 26602573 Review.
-
Cardiovascular Protective Effects of Centella asiatica and Its Triterpenes: A Review.Planta Med. 2019 Nov;85(16):1203-1215. doi: 10.1055/a-1008-6138. Epub 2019 Sep 20. Planta Med. 2019. PMID: 31539918 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of the Antioxidant Potency of Four Triterpenes of Centella asiatica against Oxidative Stress.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Apr 18;13(4):483. doi: 10.3390/antiox13040483. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38671930 Free PMC article.
-
Plants' Impact on the Human Brain-Exploring the Neuroprotective and Neurotoxic Potential of Plants.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Oct 7;17(10):1339. doi: 10.3390/ph17101339. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39458980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Centella asiatica and Its Triterpenes: A Review.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Sep 4;11:568032. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.568032. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33013406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ethnobotany, Phytochemistry and Pharmacological Features of Centella asiatica: A Comprehensive Review.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1308:451-499. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-64872-5_25. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 33861456 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms in the pathogenesis of N-nitrosodimethylamine induced hepatic fibrosis.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Jan 8;10(1):18. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-1272-8. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 30622238 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jin YL, Enzan H, Kuroda N, Hayashi Y, Nakayama H, Zhang YH, Toi M, Miyazaki E, Hiroi M, Guo LM, Saibara T. Tissue remodeling following submassive hemorrhagic necrosis in rat livers induced by an intraperitoneal injection of dimethylnitrosamine. Virchows Arch. 2003;442:39–47. - PubMed
-
- Teufelhofer O, Parzefall W, Kainzbauer E, Ferk F, Freiler C, Knasmüller S, Elbling L, Thurman R, Schulte-Hermann R. Superoxide generation from kupffer cells contributes to hepatocarcinogenesis: Studies on NADPHoxidase knockout mice. Carcinogenesis. 2005;26:319–329. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgh320. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

