Veno-venous loop through coronary sinus for LV lead placement during cardiac resynchronization therapy
- PMID: 27751292
- PMCID: PMC5067787
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ihj.2016.02.023
Veno-venous loop through coronary sinus for LV lead placement during cardiac resynchronization therapy
Abstract
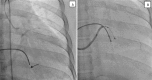
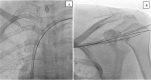
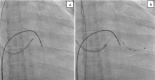
Left ventricular lead placement in the appropriate branch of coronary sinus is the key to successful cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) and this step is technically challenging. We describe a case of non-ischemic cardiomyopathy with heart failure, taken up for cardiac resynchronization therapy with defibrillator (CRT-D) implantation. The quadripolar left ventricular lead was impossible to advance into the target lateral branch of the coronary sinus. We made a veno-venous loop, advancing the coronary guidewire through the middle cardiac vein to coronary sinus and then to superior vena cava. The guidewire then snared through the same left subclavian vein and exteriorized. Over this loop, the left ventricular lead of the CRT-D device was implanted successfully. This novel approach can be used to successfully implant the LV lead in difficult to implant situations, obviating the need for thoracotomy or other methods of LV lead implantation.
Keywords: Coronary sinus; LV lead; Snare; Veno-venous loop.
Copyright © 2016 Cardiological Society of India. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Abraham W.T., Hayes D.L. Cardiac resynchronization therapy for heart failure. Circulation. 2003;108:2596–2603. - PubMed
-
- Worley S.J., Gohn D.C., Pulliam R.W. Goose neck snare for LV lead placement in difficult venous anatomy. PACE. 2009;32:1577–1581. - PubMed
-
- Rafael A., West M.B. Coronary venous floss: a novel technique for left ventricular lead positioning in cardiac resynchronization therapy. J Innov Cardiac Rhythm Manag. 2012;3:988–991.
-
- Magalhaes A., Menezes M., Cortez-Dias N., de Sousa J., Marques P. Snare system for left ventricular lead placement in cardiac resynchronization therapy. Rev Port Cardiol. 2015;34:221–222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

