Inflammation and Lymphedema Are Exacerbated and Prolonged by Neuropilin 2 Deficiency
- PMID: 27751443
- PMCID: PMC5222969
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2016.07.022
Inflammation and Lymphedema Are Exacerbated and Prolonged by Neuropilin 2 Deficiency
Abstract
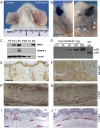
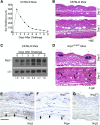
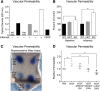
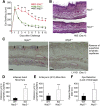
The vasculature influences the progression and resolution of tissue inflammation. Capillaries express vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptors, including neuropilins (NRPs), which regulate interstitial fluid flow. NRP2, a receptor of VEGFA and semaphorin (SEMA) 3F ligands, is expressed in the vascular and lymphatic endothelia. Previous studies have demonstrated that blocking VEGF receptor 2 attenuates VEGFA-induced vascular permeability. The inhibition of NRP2 was hypothesized to decrease vascular permeability as well. Unexpectedly, massive tissue swelling and edema were observed in Nrp2-/- mice compared with wild-type littermates after delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions. Vascular permeability was twofold greater in inflamed blood vessels in Nrp2-deficient mice compared to those in Nrp2-intact littermates. The addition of exogenous SEMA3F protein inhibited vascular permeability in Balb/cJ mice, suggesting that the loss of endogenous Sema3F activity in the Nrp2-deficient mice was responsible for the enhanced vessel leakage. Functional lymphatic capillaries are necessary for draining excess fluid after inflammation; however, Nrp2-mutant mice lacked superficial lymphatic capillaries, leading to 2.5-fold greater fluid retention and severe lymphedema after inflammation. In conclusion, Nrp2 deficiency increased blood vessel permeability and decreased lymphatic vessel drainage during inflammation, highlighting the importance of the NRP2/SEMA3F pathway in the modulation of tissue swelling and resolution of postinflammatory edema.
Copyright © 2016 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Site-directed mutagenesis in the B-neuropilin-2 domain selectively enhances its affinity to VEGF165, but not to semaphorin 3F.J Biol Chem. 2007 Aug 31;282(35):25698-707. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M702942200. Epub 2007 Jun 26. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17595163
-
Hypoxia induces tumor and endothelial cell migration in a semaphorin 3F- and VEGF-dependent manner via transcriptional repression of their common receptor neuropilin 2.Cell Adh Migr. 2011 May-Jun;5(3):266-75. doi: 10.4161/cam.5.3.16294. Epub 2011 May 1. Cell Adh Migr. 2011. PMID: 21610314 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of VEGF-C, semaphorin 3F, and neuropilin-2 expression in oral squamous cell carcinomas and their relationship with lymphangiogenesis.J Surg Oncol. 2015 Mar 15;111(4):382-8. doi: 10.1002/jso.23842. Epub 2014 Dec 4. J Surg Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25475162
-
Neuropilins in neoplasms: expression, regulation, and function.Exp Cell Res. 2006 Mar 10;312(5):584-93. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2005.11.024. Epub 2006 Jan 27. Exp Cell Res. 2006. PMID: 16445911 Review.
-
Neuropilin signalling in vessels, neurons and tumours.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2013 Mar;24(3):172-8. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2013.01.001. Epub 2013 Jan 11. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23319134 Review.
Cited by
-
FOXA1 exacerbates LPS-induced vascular endothelial cell injury in sepsis by suppressing the transcription of NRP2.Cytotechnology. 2024 Dec;76(6):697-707. doi: 10.1007/s10616-024-00647-w. Epub 2024 Jul 30. Cytotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39435415
-
Emerging Roles for Neuropilin-2 in Cardiovascular Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 21;21(14):5154. doi: 10.3390/ijms21145154. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32708258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Semaphorins and Their Receptors in Innate Immune Responses and Clinical Diseases of Acute Inflammation.Front Immunol. 2021 May 3;12:672441. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.672441. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34012455 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative Assessment of the Apical and Basolateral Membrane Expression of VEGFR2 and NRP2 in VEGF-A-stimulated Cultured Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells.J Histochem Cytochem. 2022 Aug;70(8):557-569. doi: 10.1369/00221554221115767. Epub 2022 Jul 25. J Histochem Cytochem. 2022. PMID: 35876388 Free PMC article.
-
The intragraft microenvironment as a central determinant of chronic rejection or local immunoregulation/tolerance.Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2017 Feb;22(1):55-63. doi: 10.1097/MOT.0000000000000373. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2017. PMID: 27898465 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Halin C., Detmar M. Chapter 1. Inflammation, angiogenesis, and lymphangiogenesis. Methods Enzymol. 2008;445:1–25. - PubMed
-
- Kunstfeld R., Hirakawa S., Hong Y.K., Schacht V., Lange-Asschenfeldt B., Velasco P., Lin C., Fiebiger E., Wei X., Wu Y., Hicklin D., Bohlen P., Detmar M. Induction of cutaneous delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions in VEGF-A transgenic mice results in chronic skin inflammation associated with persistent lymphatic hyperplasia. Blood. 2004;104:1048–1057. - PubMed
-
- Kajiya K., Detmar M. An important role of lymphatic vessels in the control of UVB-induced edema formation and inflammation. J Invest Dermatol. 2006;126:919–921. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

