Genomic Biomarkers of a Randomized Trial Comparing First-line Everolimus and Sunitinib in Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 27751729
- PMCID: PMC5431298
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.10.007
Genomic Biomarkers of a Randomized Trial Comparing First-line Everolimus and Sunitinib in Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC) patients are commonly treated with vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) inhibitors or mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors. Correlations between somatic mutations and first-line targeted therapy outcomes have not been reported on a randomized trial.
Objective: To evaluate the relationship between tumor mutations and treatment outcomes in RECORD-3, a randomized trial comparing first-line everolimus (mTOR inhibitor) followed by sunitinib (VEGF inhibitor) at progression with the opposite sequence in 471 metastatic RCC patients.
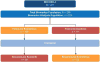
Design, setting, and participants: Targeted sequencing of 341 cancer genes at ∼540× coverage was performed on available tumor samples from 258 patients; 220 with clear cell histology (ccRCC).
Outcome measurements and statistical analysis: Associations between somatic mutations and median first-line progression free survival (PFS1L) and overall survival were determined in metastatic ccRCC using Cox proportional hazards models and log-rank tests.
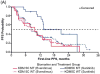
Results and limitations: Prevalent mutations (≥ 10%) were VHL (75%), PBRM1 (46%), SETD2 (30%), BAP1 (19%), KDM5C (15%), and PTEN (12%). With first-line everolimus, PBRM1 and BAP1 mutations were associated with longer (median [95% confidence interval {CI}] 12.8 [8.1, 18.4] vs 5.5 [3.1, 8.4] mo) and shorter (median [95% CI] 4.9 [2.9, 8.1] vs 10.5 [7.3, 12.9] mo) PFS1L, respectively. With first-line sunitinib, KDM5C mutations were associated with longer PFS1L (median [95% CI] of 20.6 [12.4, 27.3] vs 8.3 [7.8, 11.0] mo). Molecular subgroups of metastatic ccRCC based on PBRM1, BAP1, and KDM5C mutations could have predictive values for patients treated with VEGF or mTOR inhibitors. Most tumor DNA was obtained from primary nephrectomy samples (94%), which could impact correlation statistics.
Conclusions: PBRM1, BAP1, and KDM5C mutations impact outcomes of targeted therapies in metastatic ccRCC patients.
Patient summary: Large-scale genomic kidney cancer studies reported novel mutations and heterogeneous features among individual tumors, which could contribute to varied clinical outcomes. We demonstrated correlations between somatic mutations and treatment outcomes in clear cell renal cell carcinoma, supporting the value of genomic classification in prospective studies.
Keywords: BAP1; Everolimus; Genomic biomarker; KDM5C; Kidney cancer; PBRM1; SETD2; Sunitinib; Targeted therapy; Tumor suppressor gene.
Copyright © 2016 European Association of Urology. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Comment in
-
Linking Gene Mutations to Clinical Outcomes and Response to Therapy in Clear-cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: Ready for Prime Time?Eur Urol. 2017 Mar;71(3):415-416. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.10.034. Epub 2016 Nov 2. Eur Urol. 2017. PMID: 27816301 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Re: James J. Hsieh, David Chen, Patricia I. Wang, et al. Genomic Biomarkers of a Randomized Trial Comparing First-line Everolimus and Sunitinib in Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. Eur Urol 2017;71:405-14.Eur Urol. 2017 Sep;72(3):e72-e73. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2017.01.012. Epub 2017 Jan 17. Eur Urol. 2017. PMID: 28108150 No abstract available.
-
Reply to Ye Lei, Serdar Yildiz, and Minfeng Chen's Letter to the Editor re: James J. Hsieh, David Chen, Patricia Wang, et al. Genomic Biomarkers of a Randomized Trial Comparing First-line Everolimus and Sunitinib in Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. Eur Urol 2017;71:405-14.Eur Urol. 2017 Sep;72(3):e74-e75. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2017.01.013. Epub 2017 Jan 19. Eur Urol. 2017. PMID: 28111113 No abstract available.
References
-
- Kaelin WG., Jr The von Hippel-Lindau tumour suppressor protein: O2 sensing and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:865–73. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

