Removal of aquaporin-4 from glial and ependymal membranes causes brain water accumulation
- PMID: 27751903
- PMCID: PMC5157926
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcn.2016.10.004
Removal of aquaporin-4 from glial and ependymal membranes causes brain water accumulation
Abstract
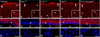
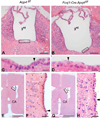
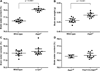
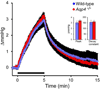
There is a constitutive production of water in brain. The efflux routes of this excess water remain to be identified. We used basal brain water content as a proxy for the capacity of water exit routes. Basal brain water content was increased in mice with a complete loss of aquaporin-4 (AQP4) water channels (global Aqp4-/- mice), but not in mice with a selective removal of perivascular AQP4 or in a novel mouse line with a selective deletion of ependymal AQP4 (Foxj1-Cre:Aqp4flox/flox mice). Unique for the global Aqp4-/- mice is the loss of the AQP4 pool subjacent to the pial membrane. Our data suggest that water accumulates in brain when subpial AQP4 is missing, pointing to a critical role of this pool of water channels in brain water exit.
Keywords: AQP4; Alpha-syntrophin; Aquaporin; Astrocytes; Brain edema; CSF; Cerebrospinal fluid; Endfeet; Ependyma; Extracellular space; Foxj1; Glia; Glymphatic; Interstitial fluid; Neuron-glial; Paravascular; Water homeostasis.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Amiry-Moghaddam M, Otsuka T, Hurn PD, Traystman RJ, Haug FM, Froehner SC, Adams ME, Neely JD, Agre P, Ottersen OP, Bhardwaj A. An alpha-syntrophin-dependent pool of AQP4 in astroglial end-feet confers bidirectional water flow between blood and brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:2106–2111. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Haj-Yasein NN, Vindedal GF, Eilert-Olsen M, Gundersen GA, Skare O, Laake P, Klungland A, Thoren AE, Burkhardt JM, Ottersen OP, Nagelhus EA. Glial-conditional deletion of aquaporin-4 (Aqp4) reduces blood-brain water uptake and confers barrier function on perivascular astrocyte endfeet. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:17815–17820. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Iliff JJ, Wang M, Liao Y, Plogg BA, Peng W, Gundersen GA, Benveniste H, Vates GE, Deane R, Goldman SA, Nagelhus EA, Nedergaard M. A paravascular pathway facilitates CSF flow through the brain parenchyma and the clearance of interstitial solutes, including amyloid beta. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4:147ra111. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

