Getting the right balance: insole design alters the static balance of people with diabetes and neuropathy
- PMID: 27752287
- PMCID: PMC5053070
- DOI: 10.1186/s13047-016-0172-3
Getting the right balance: insole design alters the static balance of people with diabetes and neuropathy
Abstract
Background: Over 1 in 3 older people with diabetes sustain a fall each year. Postural instability has been identified as independent risk factor for falls within people with Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy (DPN). People with DPN, at increased risk of falls, are routinely required to wear offloading insoles, yet the impact of these insoles on postural stability and postural control is unknown. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of a standard offloading insole and its constituent parts on the balance in people with DPN.
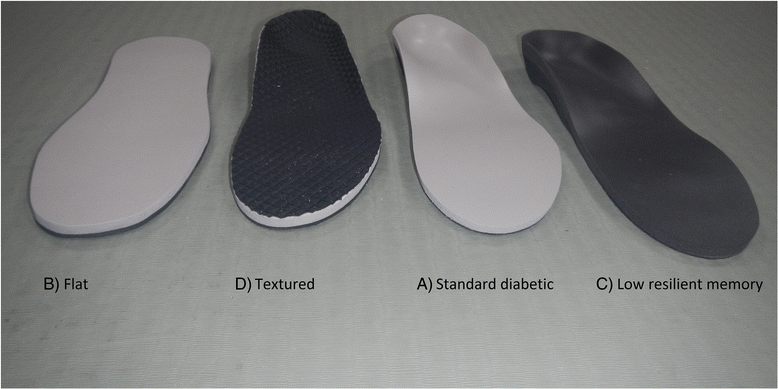
Methods: A random sample of 50 patients with DPN were observed standing for 3 × 30 s, and stepping in response to a light, under five conditions presented in a random order; as defined by a computer program; 1) no insole, 2) standard diabetic: a standard offloading insole made from EVA/poron®, and three other insoles with one design component systematically altered 3) flat: diabetic offloading insole with arch fill removed, 4) low resilient memory: diabetic offloading insole with the cover substituted with low resilience memory V9, 5) textured: diabetic offloading insole with a textured PVC surface added (Algeos Ltd). After each condition participants self-rated perceived steadiness.
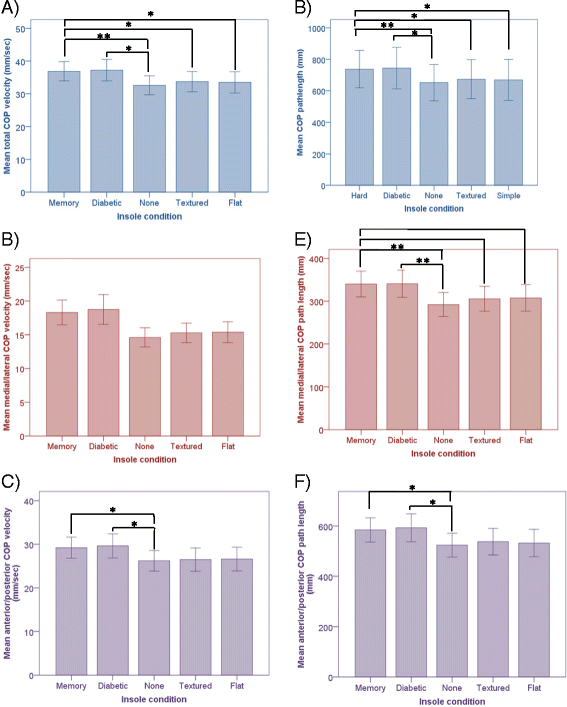
Results: Insole design effected static balance and balance perception, but not stepping reaction time in people with DPN. The diabetic and memory shaped insoles (with arch fill) significantly increased centre of pressure velocity (14 %, P = 0.006), (13 %, P = 0.001), and path length (14 %, P = 0.006), (13 %, P = 001), when compared to the no insole condition. The textured shaped and flat soft insole had no effect on static balance when compared to the no insole condition (P > 0.05).
Conclusion: Insoles have an effect on static balance but not stepping reaction time. This effect is independent of neuropathy severity. The addition of a textured cover seems to counter the negative effect of an arch fill, even in participants with severe sensation loss. Static balance is unaffected by material softness or resilience. Current best practice of providing offloading insoles, with arch fill, to increase contact area and reduce peak pressure could be making people more unstable. Whilst flat, soft insoles maybe the preferable design option for those with poor balance. There is a need to develop an offloading insole that can reduce diabetic foot ulcer risk, without compromising balance.
Keywords: Diabetic; balance; insoles; neuropathy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effects of wearing textured versus smooth shoe insoles for 4-weeks in people with diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a randomised controlled trial.Disabil Rehabil. 2025 Feb;47(3):751-761. doi: 10.1080/09638288.2024.2360658. Epub 2024 May 31. Disabil Rehabil. 2025. PMID: 38819206 Clinical Trial.
-
Footwear and insole design features that reduce neuropathic plantar forefoot ulcer risk in people with diabetes: a systematic literature review.J Foot Ankle Res. 2020 Jun 4;13(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s13047-020-00400-4. J Foot Ankle Res. 2020. PMID: 32498719 Free PMC article.
-
Custom-Made Ethyl Vinyl Acetate Insoles with Arch Support Could Improve Static Balance in Diabetic Women with Neuropathic Foot.J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2023 May-Jun;113(3):20-222. doi: 10.7547/20-222. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2023. PMID: 37463186
-
The effects of vibrating shoe insoles on standing balance, walking, and ankle-foot muscle activity in adults with diabetic peripheral neuropathy.Gait Posture. 2024 Jun;111:8-13. doi: 10.1016/j.gaitpost.2024.04.008. Epub 2024 Apr 9. Gait Posture. 2024. PMID: 38603968 Clinical Trial.
-
Footwear and insole design features for offloading the diabetic at risk foot-A systematic review and meta-analyses.Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2020 Apr 11;4(1):e00132. doi: 10.1002/edm2.132. eCollection 2021 Jan. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2020. PMID: 33532602 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The effect of calcaneus and metatarsal head offloading insoles on healthy subjects' gait kinematics, kinetics, asymmetry, and the implications for plantar pressure management: A pilot study.PLoS One. 2024 May 17;19(5):e0303826. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0303826. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38758937 Free PMC article.
-
Textured shoe insoles to improve balance performance in adults with diabetic peripheral neuropathy: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.BMJ Open. 2019 Jul 17;9(7):e026240. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-026240. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 31320345 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of postural stability under single and dual task conditions in individuals with and without intellectual disability.Int J Dev Disabil. 2023 Dec 23;71(5):725-732. doi: 10.1080/20473869.2023.2280726. eCollection 2025. Int J Dev Disabil. 2023. PMID: 40687527 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanical and Thermal Behaviours of Weft-Knitted Spacer Fabric Structure with Inlays for Insole Applications.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Feb 5;14(3):619. doi: 10.3390/polym14030619. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35160608 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of offloading devices on static and dynamic balance in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A systematic review.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2021 Jun;22(2):325-335. doi: 10.1007/s11154-020-09619-9. Epub 2021 Jan 16. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2021. PMID: 33452959 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

