P53 regulates disruption of neuronal development in the adult hippocampus after irradiation
- PMID: 27752364
- PMCID: PMC5045962
- DOI: 10.1038/cddiscovery.2016.72
P53 regulates disruption of neuronal development in the adult hippocampus after irradiation
Abstract
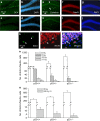
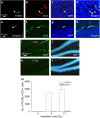
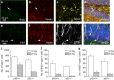
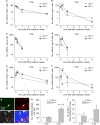
Inhibition of hippocampal neurogenesis is implicated in neurocognitive dysfunction after cranial irradiation for brain tumors. How irradiation results in impaired neuronal development remains poorly understood. The Trp53 (p53) gene is known to regulate cellular DNA damage response after irradiation. Whether it has a role in disruption of late neuronal development remains unknown. Here we characterized the effects of p53 on neuronal development in adult mouse hippocampus after irradiation. Different bromodeoxyuridine incorporation paradigms and a transplantation study were used for cell fate mapping. Compared with wild-type mice, we observed profound inhibition of hippocampal neurogenesis after irradiation in mice deficient in p53 despite the absence of acute apoptosis of neuroblasts. The putative neural stem cells were apoptosis resistant after irradiation regardless of p53 genotype. Cell fate mapping using different bromodeoxyuridine incorporation paradigms revealed enhanced activation of neural stem cells and their consequential exhaustion in the absence of p53 after irradiation. Both p53-knockout and wild-type mice demonstrated similar extent of microglial activation in the hippocampus after irradiation. Impairment of neuronal differentiation of neural progenitors transplanted in irradiated hippocampus was not altered by p53 genotype of the recipient mice. We conclude that by inhibiting neural progenitor activation, p53 serves to mitigate disruption of neuronal development after irradiation independent of apoptosis and perturbation of the neural stem cell niche. These findings suggest for the first time that p53 may have a key role in late effects in brain after irradiation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of p21 on adult hippocampal neuronal development after irradiation.Cell Death Discov. 2018 Jul 18;4:15. doi: 10.1038/s41420-018-0081-2. eCollection 2018. Cell Death Discov. 2018. PMID: 30210818 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Apoptosis Radiosensitivity of Neural Progenitors in Adult Mouse Hippocampus.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jun 20;17(5):970. doi: 10.3390/ijms17060970. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27331809 Free PMC article.
-
Abrogation of early apoptosis does not alter late inhibition of hippocampal neurogenesis after irradiation.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010 Jul 15;77(4):1213-22. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.01.015. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010. PMID: 20610042
-
Research update: neurogenesis in adult brain and neuropsychiatric disorders.Mt Sinai J Med. 2006 Nov;73(7):931-40. Mt Sinai J Med. 2006. PMID: 17195878 Review.
-
A Glance of p53 Functions in Brain Development, Neural Stem Cells, and Brain Cancer.Biology (Basel). 2020 Sep 11;9(9):285. doi: 10.3390/biology9090285. Biology (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32932978 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Age-dependent changes of p53 and p63 immunoreactivities in the mouse hippocampus.Lab Anim Res. 2019 Oct 29;35:20. doi: 10.1186/s42826-019-0022-0. eCollection 2019. Lab Anim Res. 2019. PMID: 32257908 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation-induced cognitive toxicity: pathophysiology and interventions to reduce toxicity in adults.Neuro Oncol. 2018 Apr 9;20(5):597-607. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nox195. Neuro Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29045710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Turning Death to Growth: Hematopoietic Growth Factors Promote Neurite Outgrowth through MEK/ERK/p53 Pathway.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Jul;55(7):5913-5925. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0814-x. Epub 2017 Nov 8. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 29119536
-
Effects of p21 on adult hippocampal neuronal development after irradiation.Cell Death Discov. 2018 Jul 18;4:15. doi: 10.1038/s41420-018-0081-2. eCollection 2018. Cell Death Discov. 2018. PMID: 30210818 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Apolipoprotein E Genotype on Neurocognitive Function in Patients With Brain Metastases: An Analysis of NRG Oncology's RTOG 0614.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2024 Jul 1;119(3):846-857. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2023.12.004. Epub 2023 Dec 13. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2024. PMID: 38101486 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhao C, Deng W, Gage FH. Mechanisms and functional implications of adult neurogenesis. Cell 2008; 132: 645–660. - PubMed
-
- Shors TJ, Miesegaes G, Beylin A, Zhao M, Rydel T, Gould E. Neurogenesis in the adult is involved in the formation of trace memories. Nature 2001; 410: 372–376. - PubMed
-
- Feng R, Rampon C, Tang YP, Shrom D, Jin J, Kyin M et al. Deficient neurogenesis in forebrain-specific presenilin-1 knockout mice is associated with reduced clearance of hippocampal memory traces. Neuron 2001; 32: 911–926. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

