Successful treatment of sepsis due to Pantoea agglomerans by polymyxin B-immobilized fiber column direct hemoperfusion therapy in a small cell lung carcinoma patient
- PMID: 27752466
- PMCID: PMC5061076
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2016.10.004
Successful treatment of sepsis due to Pantoea agglomerans by polymyxin B-immobilized fiber column direct hemoperfusion therapy in a small cell lung carcinoma patient
Abstract
Sepsis is a life-threatening condition caused by the inflammatory response to invading organisms. Polymyxin B-immobilized fiber column direct hemoperfusion (PMX-DHP) is used to reduce blood endotoxin levels and modulate circulating inflammatory cytokine levels in sepsis patients. Here we report that severe sepsis caused by an infection of the gram-negative bacterium Pantoea agglomerans in a patient with small cell lung carcinoma was treated successfully with antibiotics and PMX-DHP. The patient, a 49-year-old Japanese male smoker whose condition was complicated with hyponatremia due to SIADH (syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone), rapidly developed sepsis and disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) after the administration of cisplatin and irinotecan. Despite initial antibiotics therapy, severe host responses including hypotension, high body temperature and tachycardia were noted. We initiated PMX-DHP, and the patient's Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score was greatly reduced and his DIC improved immediately. To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of PMX-DHP therapy for severe sepsis caused by P. agglomerans infection. Although the efficacy of PMX-DHP in sepsis is not well defined, PMX-DHP therapy should be considered in cases of sepsis from gram-negative infections.
Keywords: PMX-DHP; Pantoea agglomerans; SCLC; SIADH; Sepsis.
Figures
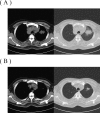


Similar articles
-
[Polymyxin-B direct hemoperfusion (PMX-DHP) in gram negative sepsis].G Ital Nefrol. 2006 May-Jun;23 Suppl 36:S94-102. G Ital Nefrol. 2006. PMID: 17068736 Clinical Trial. Italian.
-
Efficacy of direct hemoperfusion using polymyxin B-immobilized fiber column (PMX-DHP) in rapidly progressive interstitial pneumonias: results of a historical control study and a review of previous studies.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2017 Jul;11(7):261-275. doi: 10.1177/1753465817708950. Epub 2017 May 30. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2017. PMID: 28554260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Up-to-date information on polymyxin B-immobilized fiber column direct hemoperfusion for septic shock.Acute Crit Care. 2021 May;36(2):85-91. doi: 10.4266/acc.2021.00150. Epub 2021 Apr 4. Acute Crit Care. 2021. PMID: 33813808 Free PMC article.
-
Direct hemoperfusion with polymyxin B-immobilized cartridge in severe sepsis due to intestinal perforation: hemodynamic findings and clinical considerations in anticoagulation therapy.Rev Esp Quimioter. 2013 Jun;26(2):151-8. Rev Esp Quimioter. 2013. PMID: 23817653
-
Evidence and Perspectives on the Use of Polymyxin B-Immobilized Fiber Column Hemoperfusion among Critically Ill Patients.Contrib Nephrol. 2018;196:215-222. doi: 10.1159/000485725. Epub 2018 Jul 24. Contrib Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 30041230 Review.
Cited by
-
Pantoea agglomerans: An Elusive Contributor to Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Exacerbation.Cureus. 2021 Oct 7;13(10):e18562. doi: 10.7759/cureus.18562. eCollection 2021 Oct. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34760410 Free PMC article.
-
Microbiota Assessment of Fresh-Cut Apples Packaged in Two Different Films.Microorganisms. 2023 Apr 28;11(5):1157. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11051157. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37317130 Free PMC article.
-
Bloodstream Infections by Pantoea Species: Clinical and Microbiological Findings from a Retrospective Study, Italy, 2018-2023.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Dec 13;12(12):1723. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12121723. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136757 Free PMC article.
-
Pantoea agglomerans Bacteremia: Is It Dangerous?Case Rep Infect Dis. 2020 Apr 3;2020:7890305. doi: 10.1155/2020/7890305. eCollection 2020. Case Rep Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32313708 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kageyama B., Nakae M., Yagi S., Sonoyama T. Pantoea punctata sp. nov., Pantoea citrea sp. nov., and Pantoea terrea sp. nov. isolated from fruit and soil samples. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1992;42:203–210. - PubMed
-
- Christakis G.B., Perlorentzou S.P., Aslanidou M., Savva L., Zarkadis I.K. Bacteremia caused by Pantoea agglomerans and Enterococcus faecalis in a patient with colon cancer. J. BUON. 2007;12:287–290. - PubMed
-
- Cheng A., Liu C.Y., Tsai H.Y., Hsu M.S., Yang C.J., Huang Y.T., Liao C.H., Hsueh P.R. Bacteremia caused by Pantoea agglomerans at a medical center in Taiwan, 2000-2010. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2013;46:187–194. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

