Vitamin-K-Dependent Protection of the Renal Microvasculature: Histopathological Studies in Normal and Diseased Kidneys
- PMID: 27752480
- PMCID: PMC5052692
- DOI: 10.1159/000448008
Vitamin-K-Dependent Protection of the Renal Microvasculature: Histopathological Studies in Normal and Diseased Kidneys
Abstract
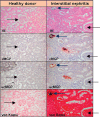
Vitamin-K-dependent carboxylation of matrix Gla protein (MGP) protects the macrocirculation against calcification. We recently reported in a multiethnic population study that the estimated glomerular filtration rate, a microvascular trait, decreased and the risk of chronic kidney disease increased with higher circulating levels of inactive dephospho-uncarboxylated MGP, a marker of vitamin K deficiency. These findings highlighted the possibility that vitamin K might have a beneficial effect on the renal microcirculation. To substantiate these epidemiological findings, we undertook a pilot study, in which we stained renal tissue samples obtained by biopsy from 2 healthy kidney donors and 4 patients with nephropathy for carboxylated and uncarboxylated MGP and calcium deposits. Three patients had renal calcifications, which were consistently associated with carboxylated and uncarboxylated MGP. Normal renal tissue was devoid of microcalcifications and staining for carboxylated and uncarboxylated MGP. Pending confirmation in a larger study covering a wider range of renal pathologies, these histopathological findings suggest that MGP might inhibit calcification not only in large arteries, as was known before, but in renal tissue as well, thereby highlighting potentially new avenues for promoting renal health, for instance by vitamin K supplementation.
Keywords: Calcification; Kidney; Matrix Gla protein; Microcirculation; Vitamin K.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of vitamin K2 supplementation on functional vitamin K deficiency in hemodialysis patients: a randomized trial.Am J Kidney Dis. 2012 Feb;59(2):186-95. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2011.10.041. Epub 2011 Dec 9. Am J Kidney Dis. 2012. PMID: 22169620 Clinical Trial.
-
The role of vitamin K in soft-tissue calcification.Adv Nutr. 2012 Mar 1;3(2):166-73. doi: 10.3945/an.111.001628. Adv Nutr. 2012. PMID: 22516724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin K-Dependent Carboxylation of Matrix Gla Protein Influences the Risk of Calciphylaxis.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017 Jun;28(6):1717-1722. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2016060651. Epub 2017 Jan 3. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28049648 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating matrix Gla protein is associated with coronary artery calcification and vitamin K status in healthy women.J Nutr Biochem. 2013 Apr;24(4):624-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2012.02.012. Epub 2012 Jul 20. J Nutr Biochem. 2013. PMID: 22819559
-
[The matrix-gla protein awakening may lead to the demise of vascular calcification].Nephrol Ther. 2015 Jul;11(4):191-200. doi: 10.1016/j.nephro.2014.12.003. Epub 2015 Mar 17. Nephrol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25794931 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Role of Matrix Gla Protein in the Complex Network of Coronary Artery Disease: A Comprehensive Review.Life (Basel). 2021 Jul 24;11(8):737. doi: 10.3390/life11080737. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34440481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Altered Intestinal Microbiota on Chronic Kidney Disease Progression.Toxins (Basel). 2018 Jul 19;10(7):300. doi: 10.3390/toxins10070300. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30029499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin K-Dependent Matrix Gla Protein as Multifaceted Protector of Vascular and Tissue Integrity.Hypertension. 2019 Jun;73(6):1160-1169. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.119.12412. Hypertension. 2019. PMID: 31006332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin K Dependent Proteins in Kidney Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 29;20(7):1571. doi: 10.3390/ijms20071571. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30934817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Renal matrix Gla protein expression increases progressively with CKD and predicts renal outcome.Exp Mol Pathol. 2018 Aug;105(1):120-129. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2018.07.001. Epub 2018 Jul 6. Exp Mol Pathol. 2018. PMID: 29981754 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schurgers LJ, Cranenburg ECM, Vermeer C. Matrix Gla-protein: the calcification inhibitor in need of vitamin K. Thromb Haemost. 2008;100:593–603. - PubMed
-
- Dalmeijer GW, Van der Schouw YT, Magdeleyns E, Ahmed N, Vermeer C, Beulens JW. The effect of menaquinone-7 supplementation on circulating species of matrix Gla protein. Atherosclerosis. 2012;225:397–402. - PubMed
-
- Cranenburg EC, Brandenburg VM, Vermeer C, Stenger M, Muhlenbruch G, Mahnken AH, Gladziwa U, Ketteler M, Schurgers LJ. Uncarboxylated matrix Gla protein (ucMGP) is associated with coronary artery calcification in haemodialysis patients. Thromb Haemost. 2009;10:359–366. - PubMed
-
- Schurgers LJ, Teunissen KJ, Knapen MHJ, Kwaijtaal M, Van Diest R, Appels A, Reutelingsperger CP, Cleutjens JP, Vermeer C. Novel conformation-specific antibodies against matrix gamma-carboxyglutamic acid (Gla) protein: undercarboxylated matrix Gla protein as marker for vascular calcification. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005;25:1629–1633. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

